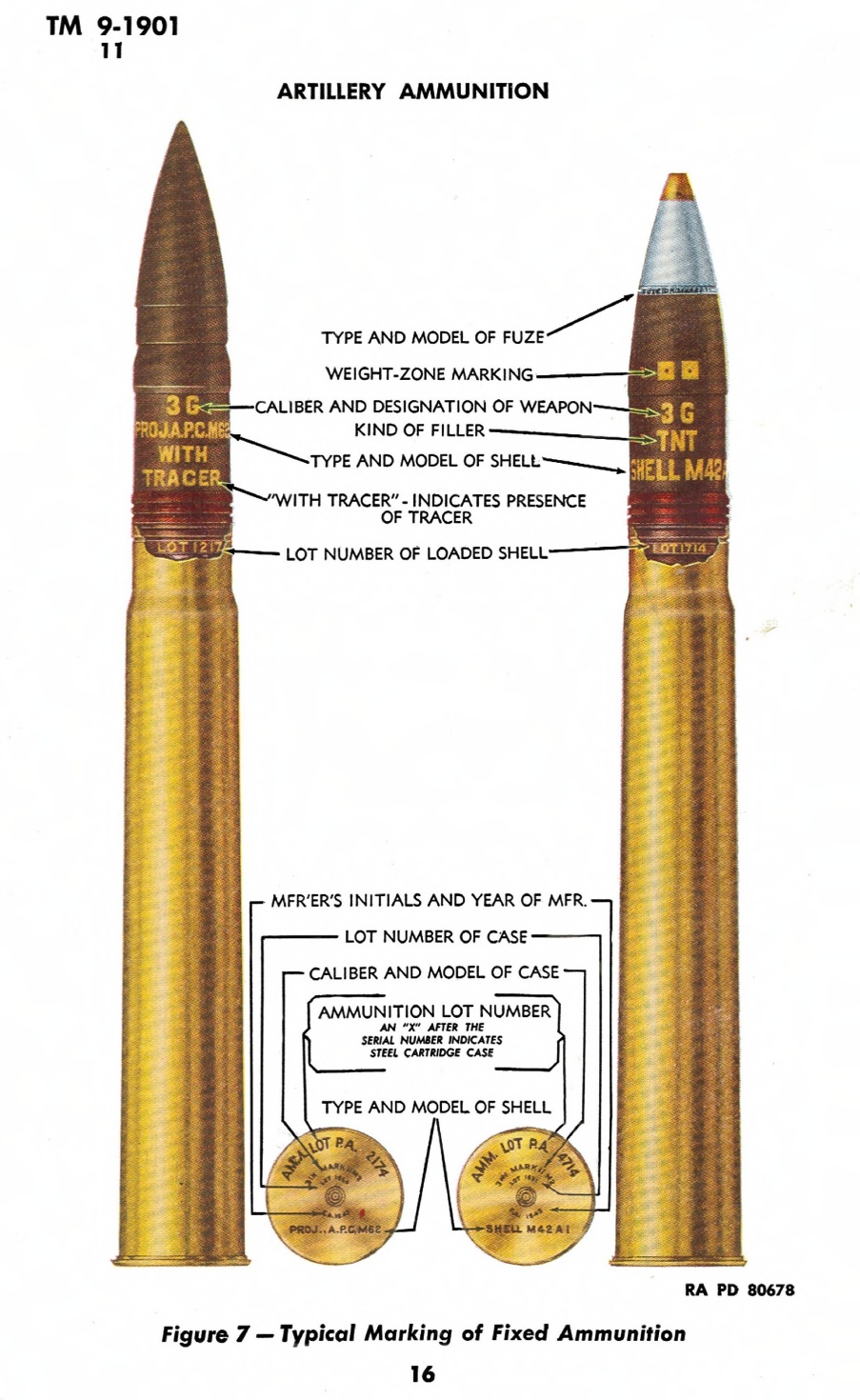
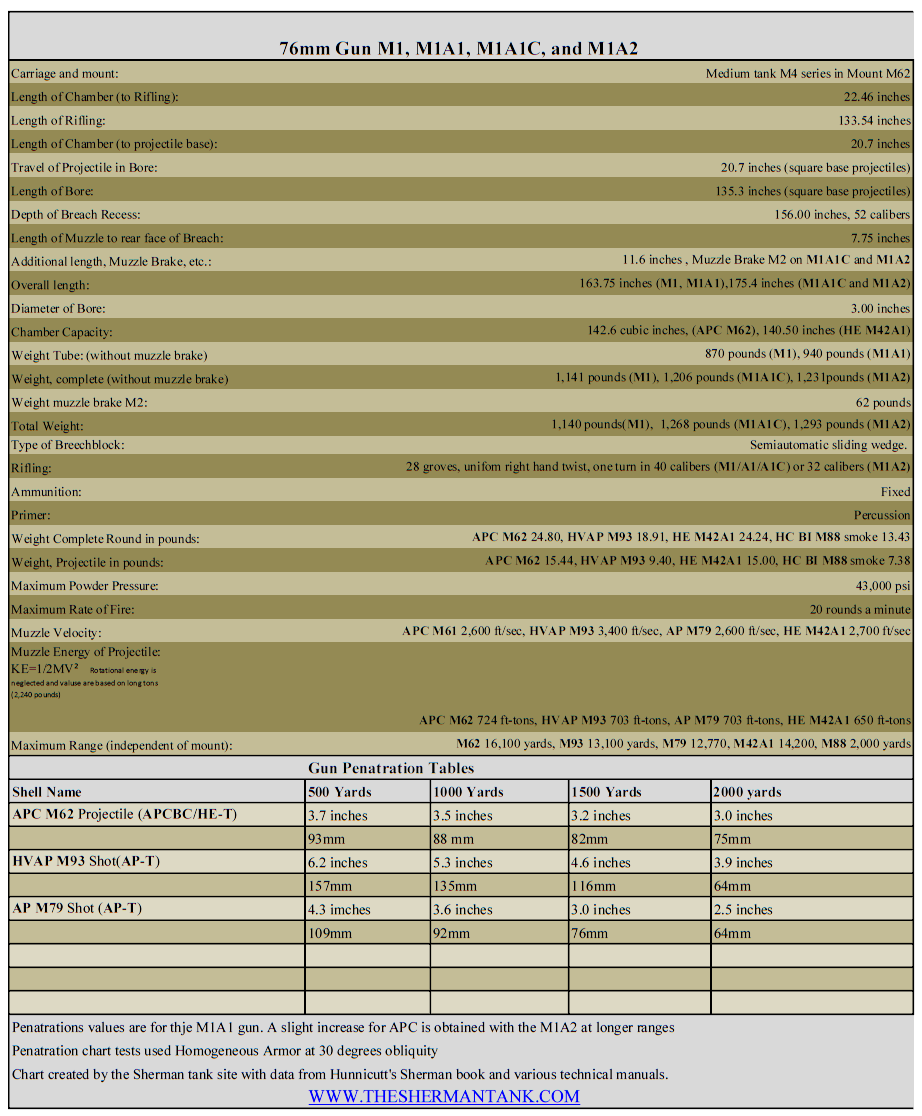
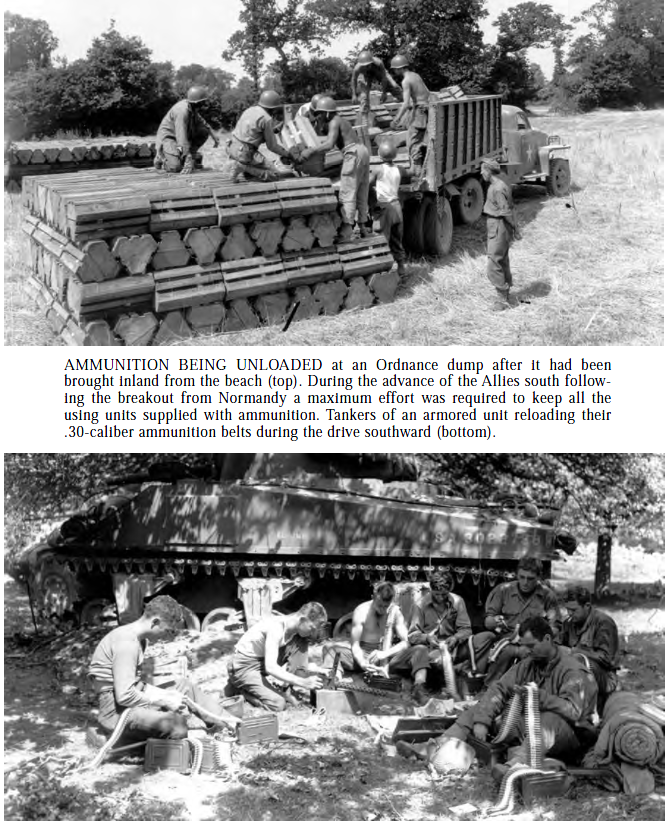
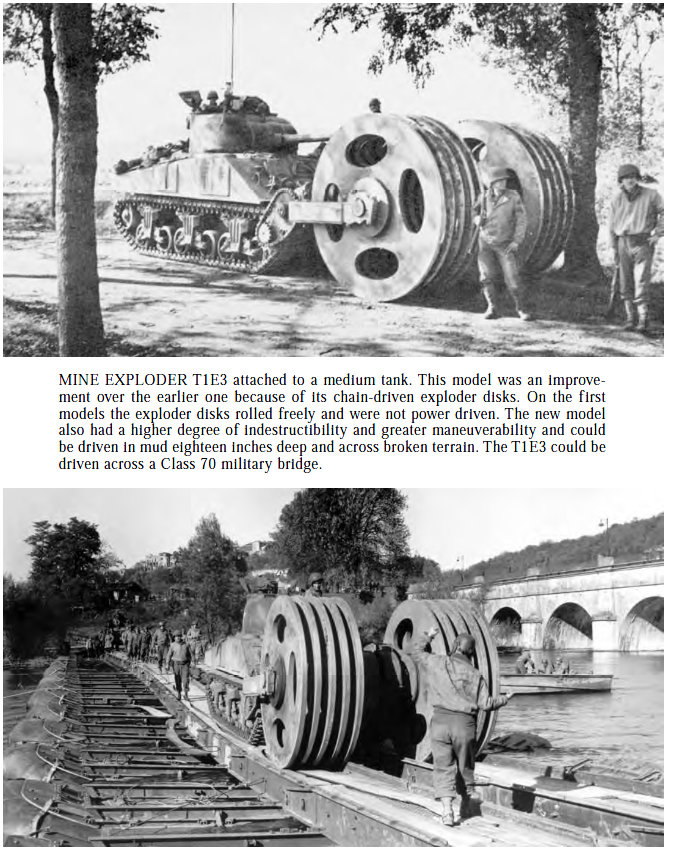
Sherman Books: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly

There have been a lot of books published on the Sherman, or WWII American Armor over the years. I have read an awful lot of these books, and I am still working to acquire more. I have all the books listed below and have read them at least once so this section can be considered part of the sources too. Anyway, from writing this section, it becomes very clear there is one very prolific writer who has spread the truth about the Sherman and done it in a hell of a lot of books. That man is Steven Zaloga, who has to be one of the most prolific writers on American Armor, if not the most, in publishing history, and he is good. It’s odd; one of the best writers seems to be overshadowed by the worst, Belton Cooper, the true villain in the slander of the Sherman.
It seems odd to me, most often when I have a conversation with a normal person about the Sherman tank(my wife says I’m weird for doing it) if they have heard of the Sherman, and read a book on it, they’ve read Deathtraps, and have never heard of Steven Zaloga, R.P. Hunnicutt, or Harry Yeide. Maybe it’s marketing, every Barnes&Noble, Borders, or another chain bookstore always had Death Traps, and any number of books on German tanks, but nothing by Zaloga and I completely missed the window Hunnicutt’s books were available, and never saw them in book stores, but I did get my copy of Deathtraps at a B&N. It wouldn’t be until his beautiful, book by Stackpole publishing, Armored Thunderbolt came out, that I saw Zaloga in a book store. Of course, now I haven’t been in a real bookstore in two years, and order most of my books online, and Steven Zaloga is all over the internet.
Let’s talk about books! While the Internet gods were frowning on me, I did a ton of reading.
Sherman, A History of the American Medium Tank by R.P. Hunnicutt: The Bible!

This book is the bible of Sherman history. It has now been reprinted and is available for 69.99 for a softbound copy, and 79.99 for a hardback. Spend the extra ten bucks, and buy it now, before it goes out of print again. Now that this book can be had for under 200$, it really is a must-buy if you have any interest in the Sherman tank or US medium tank design up to the Sherman.
This is a massive book, about twice the size of Armored Thunderbolt, but well worth the money. The books complement each other since Sherman really focuses on the Sherman, and it gets really down into the details of each Lee and Sherman sub-model. There are spec sheets in the back for each tank, the guns, and production number charts and tables showing who got what tanks via lend-lease, very exciting stuff!
This book, along with Armored Thunderbolt, and Son of a Sherman, are the three must-have Sherman books. The book comes in at 576 pages and covers the design history of each model of Lee, and Sherman, and most of the vehicles that used the M3/M4 chassis. It is filled with illustrations, and this is where I wish I had spent a little more money on the hardcover. Assuming the paper quality would be better on the hardcover books, and I’ll confirm that before I buy Firepower.
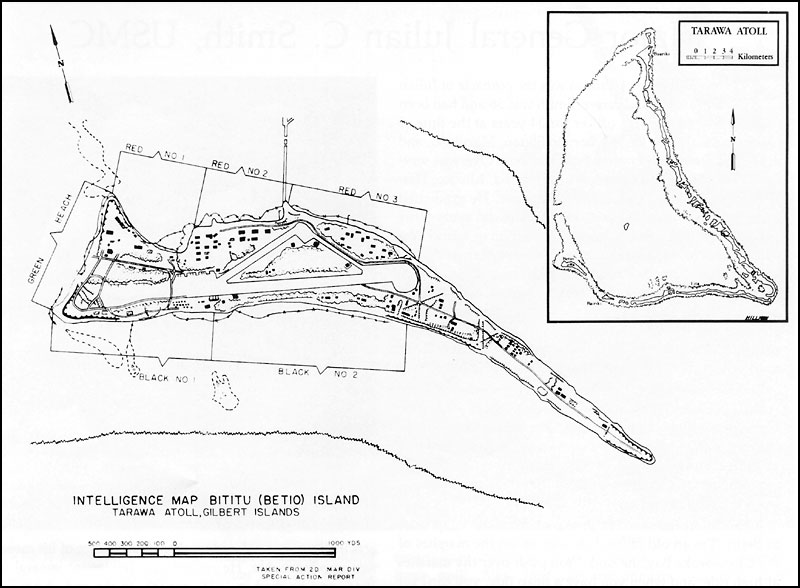
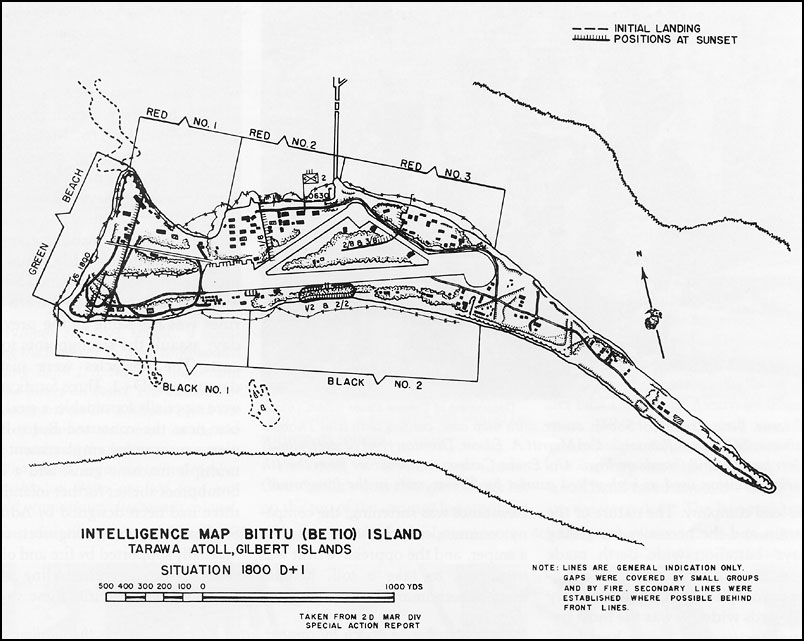
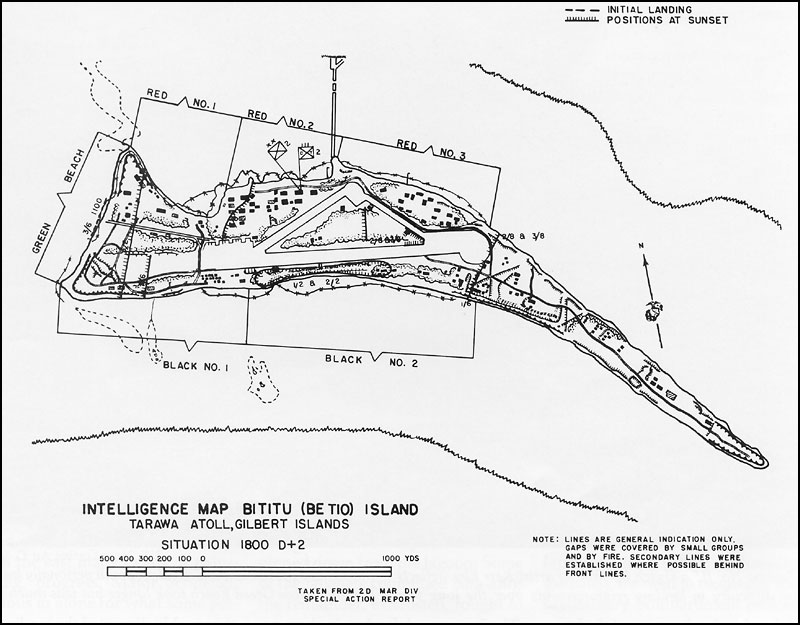
Tanks In Hell, A Marine Corps Tanks Company On Tarawa, By Oscar E. Gilbert and Romain Cansiere: A fantastic new look at the Marine tank use on Betio

This book turned out to be a great read. It covers in detail the battle for the island from the perspective of C Company First Corps Medium Tank Battalion, the only medium tank company there. Not only does it go into great detail on the Company’s actions, but it gives a solid history of the unit before and after the fight. It documents far better than anything else I’ve read, the use of Shermans by the Marines on Tarawa, and is very much worth the price. It has detailed information on what happened to each and every Sherman tank in the Company along with maps showing exactly where each tank went.
Armored Thunderbolt, The U.S. Army Sherman in World War II, by Steven Zaloga: Great book, and the best bang for the buck if you want to learn about the Sherman and the politics behind it!

I would say this is the best book on the market for the history of the Sherman, and an objective view of its performance. It does not get bogged down in the little details that can dominate a book on the Sherman but covers the history of why and how it was developed very well. It is also filled with tons of very high-quality black and white photos of the Sherman from all points in the war, including the Pacific. If there is one book you can buy, about the Sherman, this is a very good choice.
It also looks at the M4 Shermans performance, and after presenting a thorough case for why, concludes the Sherman tank was actually a better tank than the heavier German tanks it faced. A conclusion I agree with, and that is backed by data in the book.
Son of Sherman Volume 1, the Sherman Design and Development, by Stansell and Laughlin: Get This Book Before It Goes Out Of Print, It’s That Awesome. Too late it’s out of print, but still not insanely overpriced

If you want to know about the huge number of detail changes between and within model models of the Sherman, with illustrations to show you exactly how all the details differ, or you are a tank modeler and care less about the history, and more about the details of the changes in the design, this book is for you. Or you are a fan of the tank in general and buy any book on the tank you can get your hands on. Either way, buy this book. Do it now while it is still in print and a reasonable price, once it’s out of print, I bet the price gets crazy.
Well, now it’s too late to buy it while it’s in print. Still, you can find new and used copies for 50 to 60 bucks, so it’s still not overpriced yet, but if you love the Sherman, and or build models of it, or just want to understand all the minute details, you should buy this book ASAP. I liked this book so much when one copy got slightly damaged by a cat, I bought another, and it’s still wrapped in plastic, unopened. It’s a very large book with a huge number of detailed pictures taken of surviving Shermans, with a lot of very useful detail drawings, showing all the minor changes made to each model of Sherman as they were produced.
M4 Sherman at War, by Green and Brown: An Ok Book with Some Good Info, and Some Not So Good Info.

If this book can be had cheap or is the only book you can afford, it’s ok, otherwise, this books is really not great though. It still pushes the silly Ronson myth. It also fails to really cover the Panthers true flaws that make it an inferior tank to the Sherman. It does have some nice photos and a really great Marine radio transcript. It has a lot of good color photos and is a high-quality paperback book.
Armored Attack 44&45 by Steven Zaloga: These Books Are Packed with Photos of the Sherman tank


These two books, with the same title cover 1944, the other 1945. These books show off Zaloga’s huge picture collection and there are so many photos of Shermans in US Army use you can really exercise your Sherman spotting skills with these books. Also, a must-have for a detail-focused modeler, these books are hardbound with high-quality paper and very clear photos.
I’ve personally spent hours looking through these books looking for caption info, since many of the pics in it are somewhat common NARA photos, and I have them up on the site. These books are also filled with less common photos as well and are worth the money.
Marine Corps Tank Battles in the Pacific, by Oscar Gilbert: A Must Read For Sherman Tank And Marine Tank Enthusiast.

This book covers the Marine tank battles through the whole of World war II. These books go into great detail about where, when, and how the Marines used tanks in the war. These books are a must-read if you want to understand the way Marines used tanks differently from the way the Army in Europe used them. He also published books on the Marines use of Armor in Korea and Vietnam.
The Infantry’s Armor, and Steel Victory by Harry Yeide: If You Want to know about the Independent Tank Battalions, These Are the Books


These two books cover the separate tank battalions tasked with only supporting infantry and not assigned to tank divisions. The Tank battalions saw service in the ETO, PTO, and MTO and in most cases used the M4 series while doing it. They worked in a different way than the armor division tankers, getting down and dirty with the doughs, often supporting the same regiment for months.
These books are very good reads and a must-have for anyone who really wants to get into what a Sherman tank was used for. Some of the separate tank battalions really had interesting stories. Some accomplished amazing things; others suffered terrible ordeals and others both.
Another River, Another Town, a Teenage Tank Gunners Comes of Age in Combat – 1945, by John P. Irwin

I read this book a long time ago, and what stood out was the author and his tank crew ended up crewing the one and only super Pershing. The book is 176 pages, so a pretty quick read. John Irwin was a teenager when he went through this, so the book is also about a kid who had a lot to learn about everything. Since I’m doing so much reading because the internet is down, I think I’ll read through this one again.
Tanks on the Beaches, by Robert M. Neiman and Kenneth W. Estes: A more intimate look at a Marine Tankers life.

This book was really interesting, and an entertaining enough book to keep your interest. If you want a look at what it was like to be an Officer and tanker in the US Marine Corps during WWII, this is a great book for you. This is more of a personal view of the war, and Neiman had a very interesting career in the Corps.
Commanding the Red Army’s Sherman Tanks, the WWII Memoirs of Hero of the Soviet Union, Dmitriy Loza, edited and translated by James F. Gebhardt

This 173-page book is a little dry, and I suspect it’s because it was translated from Russian, but it a very interesting look at the Sherman use with the Soviet Union, and the career of Dmitry Loza, Hero of the Soviet Union. This is a great look into both the life of Soviet tankers and their use of the M4A2 Sherman.
Cutthroats, the Adventures of a Sherman Tank Driver in the Pacific, by Robert C. Dick

This book is 247 pages and follows the author’s service in a Sherman in the pacific. Robert C. Dick had a much different experience than his Army comrades in Europe, and surprisingly from his Marine cousins in the pacific! This is a personal account of war and is not packed with technical info on the tanks, but it is a very interesting window into the life of an Army tanker in the PTO. A great weekend read, I highly recommend it.
Warrior Series 78, US Army Tank Crewman 1941-45, European Theater of Operations 1944-45, By Steven Zaloga

This book is less a detailed look at Sherman tankers, and more the story of one very famous tanker, Creighton Abrams, who commanded the 37th Tank Battalion of the 4th Armored Division, and is the namesake of the M1 Abrams MBT. It does have little sections on crew equipment, and other items to help flesh the book out a little. Still, a very interesting read, and Abrams up-armored Sherman was even the subject of a whole Dragon model kit, extra armor, and all, the tank was named Thunderbolt VII.
Warrior Series 92, US Marine Corps Tank Crewmen 1941-45 by Kenneth W Estes:

Another book in the Osprey Series, this one ‘Warrior series, volume 92’, and I think really aimed at modelers. These books are all fairly short and are meant to give a brief look into what gear and vehicles Marine tankers used during WWII. It does this well, and Mr. Estes knows his Marine history. The Marines used a lot of Shermans, and this covers their use and is a decent overview.
Battle Orders 10, US Tank and Tank Destroyer Battalions in the ETO 1944-45: Tank info for Tank Geeks

This series focuses more on unit structure than the tanks themselves. That said, you can’t really know what a Sherman tank was used for if you don’t know about the units it was deployed in. This one covers the TO&Es of Tank, tracked TD, and towed TD battalions and their tactics and was really a huge help with the Battalion section of this site.
This book is filled with very interesting charts and tables and a fair number of pictures. Well worth the price if you want to get into the details of tank and TD units.
Battle Orders 21, US Armored Units in North African and Italian Campaigns 1942-45: More Tank info for Geeks

Much like Battle Orders 10, this one gets down into how the armored units used in North Africa and Italian Campaigns. This one looks over a longer time period and has detailed tables for the earlier Lee based tank battalions and halftrack based TD units. This book has lots of charts and tables so you can really dig into what an armored unit was composed of, other than just tanks.
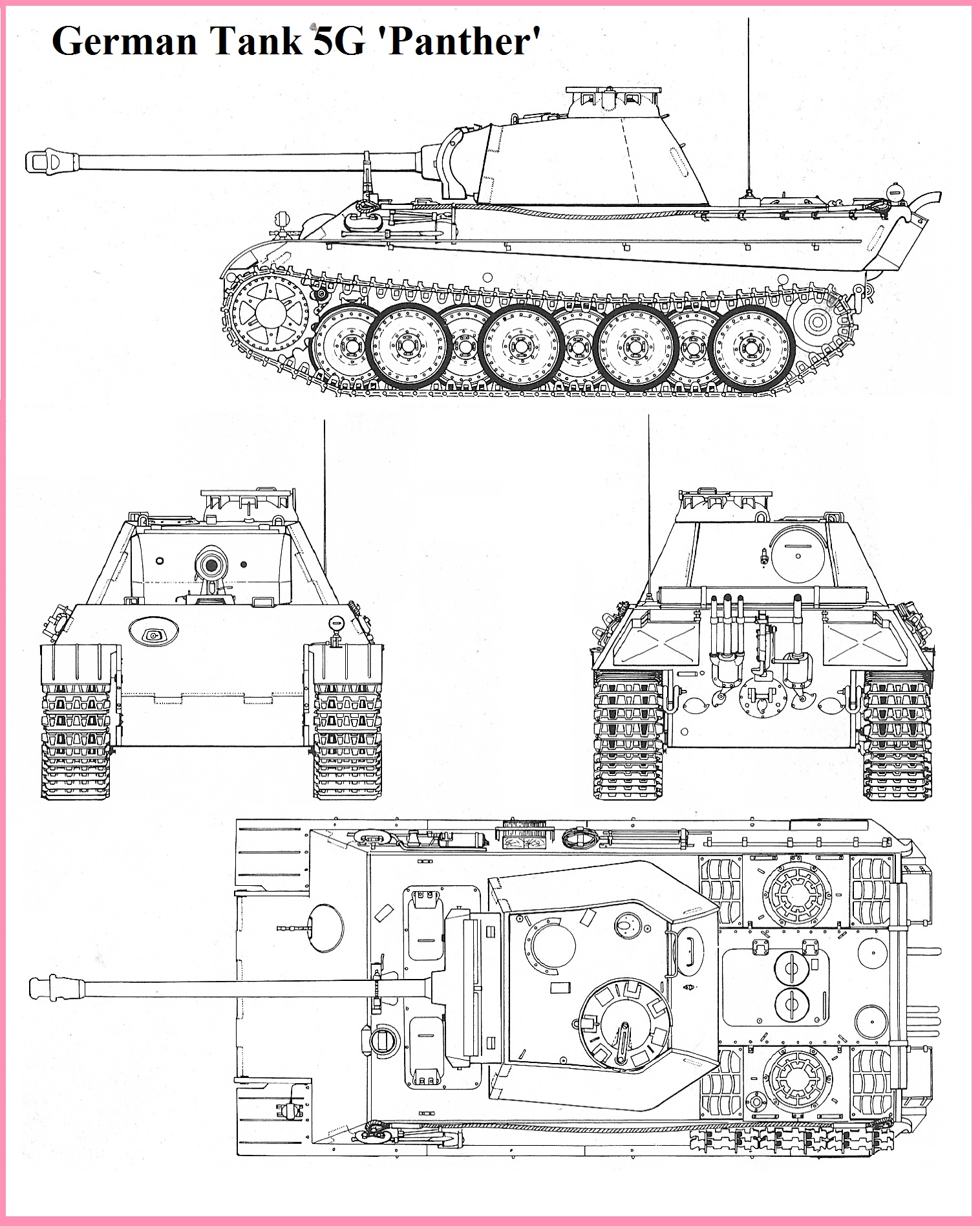
Panther VS Sherman, Battle of the Bulge 1944, By Steven Zaloga

This book disappointed me a little. I’ll read through it and take notes next time. From memory, when he talks about replacing the final drives in the panther, he says the transmission had to be pulled when it would be the sprockets, final drive housing, and several road wheels. He doesn’t point out exactly why he thinks the Panther was more technologically advanced than the Sherman, but it’s clear he thinks so. The Panther had a powerful AT gun, and good frontal armor, everything else was just poorly designed garbage waiting to break.
The Sherman had several features so advanced the Germans could not copy them, the stabilizer, the turret drive, the reliable motors, transmissions, and final drives. The transmission and final drives were good enough to work unchanged in design all the way through the M50 and M51. Even the large turret and hull castings were beyond the Germans.
Ultimately he concludes the Sherman was the better tank, so I guess it all works out in the end. Not a bad book for the price and it’s really only in deep technical areas he goes wrong, so overall worth the time and money.
Panzer IV VS Sherman France 1944, By Steven Zaloga

This is another book in the VS series, this one a little better than the Panther V Sherman book. Same format, lots of decent pics, and a better conclusion. Worth it if you can get it for a good price.
The Panzer IV and Sherman are very close tanks in capability and weight, so they make for a more interesting matchup. The Panzer IV was a better tank than the later Panther and Tiger tanks, if only because it was reliable enough to be around when needed.
Armor at War Series 7001, the M4 Sherman at War, The European Theatre 1942-1945, by Steven Zaloga

This is one of those pictorial paperbacks from the mid-90s, I picked up a ton at a garage sale, and though not the best for technical details, it does a good job for what it was designed to do. These books are aimed at armor modelers, who want close-in detail shots with unit info so they can copy the subjects. The book is 72 pages with a color drawing section, was published back in 1995.
This book is long out of print, so I wouldn’t go out of my way to find it, but if you stumble on it used and cheap, it’s a nice book to have if you like Sherman pictures. Many of these pictures can be found in other books, online, and even on this site, and in much higher resolution, but they have proved useful in improving my image captions.
Armor at War Series 7002, D-Day, Tank Warfare, Armored Combat in the Normandy Campaign, June-August 1944 by Steven J. Zaloga and George Balin

This AaWS book covers the Normandy Campaign. It is not nation-specific, so you get tanks from everyone, but there are an awful lot of Shermans in here. British Shermans, Polish Shermans, French Shermans, American Shermans, and a whole lot of knocked-out German tanks. Since this one is not focused on the Sherman, there is less here for the Sherman enthusiast, but it is still an interesting book, I just wouldn’t go out my way to find it if you just want Sherman photos.
Armor at War Series 7003, Tank Warfare In Korea 1950-53 by Steven Zaloga and George Balin: Shermans and other Tanks in Korea

Another book out of Concord Publication Company of Hong Kong, this one covering Korea, and published in 1994, and very typical of the series. The Sherman tank was used a lot in Korea, but only the M4A3 version, and for the most part HVSS tanks, with some rare exceptions.
These books have a short history section and then are filled with well caption pics. In this book’s case, if it had Armor, and was in Korea, it’s in the book.
Armor at War Series 7004, Tank Battles of the Pacific War, 1941-1945 by Steven J. Zaloga

This AaWS book is an early one, published in 1995, but it is 72 pages of awesome. This book, as the title suggests, covers tank battles in the Pacific, which means Shermans and Lees, and some light tanks here and there. There are several good books covering Armor used in the Pacific, and this book is a great companion to any of them, you will likely find higher resolution versions of photos the others books only had bad low-resolution versions in them. There is also a good number of photos of the modifications the Marines did to the Shermans for Iwo Jima. Long out of print, this can still be found used for around $20, and new for $40 or so, and for a Shermanaholic, this is a very nice book. For a bonus, this one even covers Chinese use of the Sherman M4A4 at the end of the war, and Lee use in Burma.
Armor at War Series 7005, U.S. Tank Destroyers in Combat 1941-1945, by Steven Zaloga: TDs and most are based on the Sherman

This is another ‘Armor at War’ book, this one covering US Tank Destroyers for the whole war. Lots of very nice, well captioned, pictures. This one is not totally Sherman-oriented like the others practically are, but as we know, the M10 and M36 are based on the Sherman. Long out of print, if you can find it cheap it’s worth it. This one is 75 pages and came out in 1996.
Armor at War Series 7008, Tank Battles of the Mid-East (1) the Wars of 1948-1973 by Steven Zaloga

This AaWS book covers the battles that took place in the Middle East, mostly the wars with Israel, and its war of independence. The Israeli’s were big Sherman users, though early on, the Shermans they had were a pretty rag tag group, thrown together from hulks from all over the med. This led to at least one large hatch hull tank with an early stubby mantlet 75mm turret.
Armor at War Series 7009, Tank Battles of the Mid-East (2), the wars of 1973 to present, by Steven Zaloga

This one is typical AaWS, with 73 pages and the color drawing plates with a small history section. There are still a few Sherman based vehicles that show up in this book, and that’s why it got mentioned here. Ok so maybe there is only one Sherman pic in this one, which still counts.
Armor at War Series 7032, US Amtracs and Amphibians at War, 1941-45 by Steven Zaloga and George Balin: Shermans can Swim!

This one seems like an odd choice for a section about Sherman books, but as we know, they had amphibious Shermans, and they are covered in this book. This is a typical AaWs book with 73 pages, a small history section, a color plate section, and lots of pictures, with detailed captions.
Armor at War Series 7036, The M4 Sherman at War (2), The US Army in the European Theater 1943-45, by Steven Zaloga: More Shermans, more War

This book is a follow-on to 7001, reviewed above, and is pretty much the same thing with different photos, and came out in 2001. All the things said about the first one apply. There are some nice pictures of up-armored Shermans I have not seen in many other places in here so it is worth the look if you love looking at old photos.
Armor at War Series 7038, US light Tanks at War, 1941-45 by Steven Zaloga: Light Tanks are not Shermans, but they did work together

Lots and lots of pictures of light tanks with a few pages of history on them, a nice source of pictures for any modeler and an interesting afternoon read. It focuses on the M3 and M5 lights, but other models like the M24 show up too. It has a nice color panel with drawings of various famous lights.
Armor at War Series 7042, Panzers of the Ardennes Offensive 1944-45 by Tom Cockle: The Bulge from the German perspective

This book comes in at 73 pages and was published in 2003, and gives the German perspective on the Battle of the Bulge. There is a few pages of text on the battle, and then a lot of pictures of the German tanks and other units involved, and my impression from looking through it was, almost all of it was knocked out, broken down, or abandoned. There are a surprisingly large number of Sherman pics, both functional and knocked out.
Armor at War Series 7045, The Battle of the Bulge, by Steven Zaloga

AaWS 7042 covered the Bulge from the German side, this one is more American and allied centric. Typical of the series, it has tons of black on white photos with informative captions and a small section of color drawings and a small history section. This one has some interesting photos of Creighton Abrams’s Thunderbolt tanks since he upgraded through a lot of Shermans while in command of the 37th tank Battalion.
Armor At War Series 7046, US Tank Battles in Germany 1944-45 by Steven Zaloga: More US Armor pictures!

Another Concord Publication with a short history section, and lots of pictures. This one has some late war tanks like the M24 Chaffee, and M26 Pershing. It also has a fair number of German tanks pictured as well.
Armor at War Series 7050, US Tank Battles in France 1944-45, by Steven Zaloga

This AaWS book is pretty typical of the series, this one covering the battles in France, from D-Day in Normandy until operation Nordwind and the approach of the Westwall. Lots of Shermans, lots of other American Armor, and lots of knocked out and broken down German Armor. This one also has the color drawing section and a history section in the beginning and is 74 pages. One interesting thing mentioned in this one, in the color drawing section, is a French Jumbo Sherman used by the 2e Escadron, 2e Regiment de Chasseurs d’Afrique, 6th Army Group, Alsace, 1945. I’ve never read anything about that before.
Armor at War Series 7051, US Tank Battles in North Africa and Italy, 1943-45 by Steven Zaloga

This is another one in the AaWs books, this one on US tanks in the MTO. This one has a lot of images of the M3 Lee in US use. This is another one I found extra interesting since most coverage of WWII really focuses on Western Europe. A mix of Sherman and Lee is desert and mountain terrain can be found in this one, along with just about all the armored vehicles used by the US Army. There are also a fair number of photos of knocked-out Tiger tanks, some abandoned ones too, and a few broken down. One of these Tigers was knocked out in a close-range duel with an M4A1 75 Sherman, commanded by Lieutenant Edwin Cox of the 752 tank battalion. He was awarded the Silver Star for the action, this is detailed out on page 61.
Armor at War Series 7052, US Armored Funnies, Us Specialized Armored Vehicles in the ETO in WWII, by Steven Zaloga

This Concord Publication is on US Funny tanks, things like Recovery vehicles, Prime movers, Combat Engineer Vehicles, Mine Clearing tanks, Bridging Tanks, Amphibious Tanks, CDL tanks, Flame tanks, and Rocket tanks. It has the same 73-page format with lots of pictures and a few color drawings. If you want to produce a funny in plastic, or just want to know what they looked like, or see them in action, this is a great little book.
Armor at War Series 7055, Panzers in the Gunsights, German AFVs in the ETO 1944-45 in US Army Photos, by Steven Zaloga

In one way this is your typical Concord Publication, 74 pages, a few color drawings, a little history section, and a lot of pictures with detailed captions. What sets this one apart is the pictures of German tanks, knocked out or captured by the US Army. Several of these captured tanks survive today in museums or holding lots waiting for one. One aspect that shouldn’t be a surprise to anyone who actually knows about German armor, but might be to those with more superficial knowledge on the subject, is how many were abandoned due to lack of fuel or just breaking down, and there is a lot of photographic evidence of it in this book.
Armor at War Series 7062, British Sherman Tanks by Dennis Oliver: A very nice pictorial overview

This book is a lot like the previous two ‘Armor at War books’ on the Sherman, but this one covers British use. This book had a lot of Sherman photos I have not seen before in it. It came out in 2006, and is 73 pages and well worth it if you want an exclusive look at UK Shermans. If your building a Sherman used by the UK from plastic, you’ll want this book.
Armor at War Series 7068, British Armor in Sicily and Italy, by Dennis Oliver

Like AaAs 7062m this one covers British Armor, just not the Sherman exclusively and in Italy and Sicily. Many of these images I had not seen before, and that is the real value of these books. This book, even though it is not specifically about the Sherman, is packed with pictures of the Sherman and things based on its chassis.
New Vanguard 3, Sherman Medium Tank 1942-45, by Steven Zaloga and Peter Sarson: This book covers both the 75 and 76 tanks, but not overly well

This book is an early New Vanguard book and shares a lot with NV 73, which focusses just on 76mm Shermans. I would say this is the least useful New Vanguard or Vanguard book on the Sherman at this point. The subject material and pictures can be found in later works.
New Vanguard 57, M10 and M36 Tank Destroyers 1942-53, By Steven J. Zaloga

This NV book covers the M10 and M36 in their typical format, 50 or so pages some color drawings, and a cutaway. It covers the history of US tank destroyers up to the M10, including the ones that never made it into production, and all the models of the M36. This also covers the Achilles or M10C, and post-war use of both TDs.
New Vanguard 73, M4 (76mm) Sherman Medium Tanks 1943-65 by Steven J. Zaloga: Typical NV book on the 76 Sherman

This book is part of Osprey’s New Vanguard series, volume 73 in fact. This book is pretty short but gets a decent amount of the 76mm Sherman story into it. These books are really aimed at modelers, and people into less detailed history. It does have some great charts in it. I bought this book years ago as a young teen while building models. Well worth the price if you can get it for less than 15 bucks.
New Vanguard 123, Swimming Shermans, Sherman DD amphibious tanks of World War II by David Fletcher: Nice info on how to make a tank float

Fifty-one pages on this history of the Sherman DD, but not just the Sherman, but pretty much all DD tanks, since they led up to the Sherman. Very British-centric, but they really did all the work on the DD Shermans, so it makes sense. Even though they used different versions of the Sherman for DDs than the US, the US versions are covered. Typical of the new vanguard series, best if bought cheap considering the size, but they do pack a decent amount of info in, in spite of the size limits.
New Vanguard 141, Sherman Firefly by David Fletcher: Info on the Firefly

This 52-page book covers the history of the Firefly in surprising detail. It’s also very fair to the design compromises that had to be made for the tank to work. Well worth the money if you want a more detailed look at the history of the Firefly than this site gives.
Vanguard 15, the Sherman Tank in British Service1942-45, by John Sanders: A very informative little book

I found this book really informative since most of my Sherman history reading has been very American-centric. This book is 52 pages and was first published in 1982, and gives a surprisingly fair view of the Sherman considering the time period it was written.
This book like all Vanguard books ‘regular’ and ‘new’, have a format, and that includes a color drawing section. The cover art on this one is notable for how horrible it is. I mean it is one of the worst drawings of a Sherman Firefly I have ever seen, but luckily the content is much better than the cover art. It has a very interesting section on British crew opinions and some very interesting drawings made by crews during the war. If you can find this book for a reasonable price, it’s a good one.
Vanguard 26, The Sherman Tank in Allied Service by Steven Zaloga: About as much info as you can pack info 51 pages on the Sherman

This book comes in at 51 pages, and was published in 1982, with that in mind, his later works have both updated information, and more of it, but this book was pretty darn good for when it came out. Typical of the Vanguard books, it has a color drawing section and covers the Shermans use into Korea. Long out of print, a nice find, if found cheap.
Osprey Modelling 35, Modelling the US Army M4 (75mm) Sherman Medium Tank, by Steven Zaloga

This book, along with the recommended kits and paints, etc., would be all you need to create a work of art in plastic. Mr. Zaloga is a very talented modeler, and this book is his attempt to show us, regular folks, how to produce a good-looking Sherman kit. I only wish I had known about these when I got back into building kits again.
These books are great if you want to really improve your plastic modeling skills and see how to fix flaws in some older Sherman kits. They come in at 86 pages, review the quality of many different 75mm Sherman kits and give an overview of the 1/35 scale 75mm Sherman plastic scene, though it is a tad out of date now since it’s over a decade old, and there have been many improvements to the available Sherman kits out there.
Osprey Modelling 40, Modelling the US Army (76mm) Sherman Medium Tank by Steven Zaloga

This book is the follow-up to his book on modeling the 75mm Sherman. This one was published in 2007 and includes a little info on Tasca suspensions, but predates their full kits or their change to the Asuka brand name. This covers improving the better kits on the market, a small history on the tanks, and some very advanced techniques for improving or even scratch building things for your Sherman kits. Steven Zaloga is an extremely talented modeler, and he shares step by step some of his best methods for producing these amazing kits.
Tanks Illustrated No. 11, Patton’s Tanks, by Steven Zaloga: A picture book on Patton’s tanks

This book has a short intro and then focuses on photos of the various units Paton commanded and some personal pictures of the man. It was published in 1984 and is 66 pages. It follows Patton and his various commands through the whole war and has many interesting pictures I have not seen before. If you can find it cheap it is not a bad book for what it is.
Warmachines N4, Military Photo File 555, Israeli M4 Sherman and Derivatives, by Francois Verlinden and Willy Peters

A very interesting book on Israeli Shermans and all the things they used the hulls for. This book will be very useful when I expand the Israeli Sherman section. One thing to keep in mind about this book is, it uses Israeli designations for their tanks and does not take into account, just like Israel in most cases, what the tank was to start within US designation. An example of this is all M1A1 Armed Shermans are called Sherman M1s whether it’s an M4A1 or M4A3. This book would be very useful for anyone trying to build an Israeli Sherman but is only 37 pages, and I’ve never heard of the publisher or seen other books by them.
Squadron/Signal Publications 6038, Armor in Korea, a Pictorial History by Jim Mesko

This book is 80 pages and was published in 1984. It covers armor used in Korea by all the participants. It has a small color plate section. These books are aimed at modelers and were found mostly in hobby shops. They are filled with photos with detailed captions. The Sherman was still in heavy use in Korea, and there are many pictures and captions of it being used in this book. It covers their use with Tiger faces painted on them and why it was done. Well worth it if you can find it cheap.
Squadron/Signal Publications 6090, U.S. Armor Camouflage and Markings World War II, by Jim Mesko

Anyone who has spent any time in a Hobby Shop with a plastic model section has probably seen books by Squadron/Signal. They have had an ‘At War’ Series of books for years covering just about everything military. They were not particularly long books, but they were cheap and had lots of detail shots aimed at the plastic modeler. This book is a larger format softcover, with more info, covering US Armor markings, MTO, ETO, and the PTO for the war. This book comes in at 67 pages and has a color drawing section highlighting specific common vehicles.
Squadron/Signal Publications 2016, Sherman in action, Armor NO. 16 by Bruce Culver

This is your classic Squadron Signal paperbound book on the Sherman, with lots of black and white photos covering each model of the tank. These books were all around 49 pages and had a color drawing centerfold. Back in the day they ran 5 or 6 bucks and were the perfect cheap book to go with that new model kit. Most including this one are still in print. These books have very basic info, but it’s generally accurate.
Squadron/Signal Publications 2033, M3 Lee/Grant in action, Armor NO. 33 by Jim Mesko

This is the Armor book on the M3 Lee, like its Sherman counterpart reviewed above; it’s filled with black and white photos, most showing good detail. These books are aimed at being a cheap way for a modeler to get some good photos and basic info on their subject. The small amount of technical info is generally accurate as are the captions. I bet sales on these books have dropped off since the internet really took off, you can find all the info and just about all the photos online and in higher resolution. These books will always have a soft spot for me since I still have all the ones I bought for Christmas and birthday money as a kid in the 80s!
Squadron/Signal Publications 2036, U.S. Tank Destroyers in Action, Armor Number 36 by Jim Mesko

This 51-page book on US TDs is pretty good for what it is. It covers the M3 75mm GMC, the M6 37mm GMC, the M10, Achilles IIC, the M36 and M18 Hellcat. This book cleared up what an M6 was, I ran into a reference to it in another book but had never heard of it. It saw very short use in North Africa, but slightly longer use in the PTO apparently. This book has a two-page color drawing insert and for its size is packed with good info.
Squadron /Signal Publications 2038, U.S. Self-Propelled Guns in Action, Armor NO. 38 by Jim Mesko

This 52-page book covers the M7, M12, M40, and M43, plus the Sexton. It has the 2-page color insert standard for this series and a lot of black and white photos with good captions. It also has line drawings of specific components to help modelers with fine details. All these SPG are based on the Sherman, so that’s why this one is here. It does also cover the Chaffee based M37/M41 SPG as well.
Squadron /Signal Publications 5701, Walk Around M4 Sherman, armor walk around number 1, by Jim Mesko

These books are the same format as the in-action books, but with more pages, and close up pictures so you can really see the details of the tank’s components. This one came in at 79 pages it still falls short of really covering all the details on the Sherman. It’s not really the fault of the book, the subject just has such a huge scope, you really need a book the size of Son of a Sherman to cover it. If you can’t find or afford Son of a Sherman, this is a good alternative.
Squadron /Signal Publications 6096, Tank Warfare on Iwo Jima, by David Harper

This 98-page book covers the tanks used on Iwo Jima and I have to say, it is a pretty awesome book. Not only does David Harper cover the tanks, but how the tank crews lived, and how they worked in the rear on the tanks. I had never heard of the ‘bachelor pad,’ basically, a bunker made under the tank, when they were not on the line, where the slept, they would carefully back out of these spots in the morning, so they wouldn’t have as much set up when the days fighting was done.
The tank use on Iwo Jima was extensive, and more than one Marine Tank Battalion saw action there. The fact the Sherman played a key role in the Marine Island assaults is usually not covered very well, but this book does a great job. The Japanese knew just how important the Sherman was and went to great lengths to destroy disabled Shermans, how they did is covered in here as well as all the modifications the Marines made to their tanks to safeguard them, and has a lot of photos of these modifications. This book is really a must have
Images Of War SPECIAL, M4 Sherman, by Pat Ware

This book is a real mixed bag. I’ve never bought any of the books in the series, since picture books generally are pretty fluff filled if you want hard info, and I already have a lot of Sherman pictures. I got an Amazon gift card from my mom for my Birthday, and decided to have a look and bought a used copy through them. It has a lot of images with captions, that are mostly correct, and I don’t recall any huge errors in the technical stuff, but I read it awhile back and will have to re-review to make sure. The section on the Sherman in combat is just bad. It’s full of all the old, bad, junk history spawned by the late 60s and 70 board games and junk books like Death Traps.
The truth about WWII tank warfare has been made a lot more clear in the past few years, and books like this that continue to push the old inaccurate information should be revised. With that in mind, I would not recommend spending the 25$ price for this book. If you see it cheap used and want a decent picture book, then maybe, but it should be very cheap if you go this route. The book comes in at 137 pages.
The Sherman, an Illustrated History of the M4 Medium Tank, by Peter Chamberlain and Chris Ellis.

This book was first published in 1967 or 68, and maybe the first book dedicated to a specific type of tank and was put out by Arco publishing. It is a nice little book on the M4 with a surprising amount of info packed into a small packed. I picked up my copy for a few bucks used, and wouldn’t pass up the opportunity to buy it if I saw it cheap again.
Death Traps, by Belton Cooper: This book is Crap.

Here is a great review on the subject by R. Forczyk: Death Traps, a poorly written memoir by Belton Y. Cooper promises much, but delivers little. Cooper served as an ordnance lieutenant in the 3rd Armor Division (3AD), acting as a liaison officer between the Combat Commands and the Division Maintenance Battalion. One of the first rules of memoir writing is to focus on events of which the author has direct experience; instead, Cooper is constantly discussing high-level or distant events of which he was not a witness. Consequently, the book is riddled with mistakes and falsehoods. Furthermore, the author puts his main effort into an over-simplified indictment of the American Sherman tank as a “death trap” that delayed eventual victory in the Second World War.
Cooper’s indictment of the Sherman tank’s inferiority compared to the heavier German Panther and Tiger tanks ignores many important facts. First, the Sherman was designed for mass production and this allowed the Allies to enjoy a 4-1 superiority in numbers. Second, fewer than 50% of the German armor in France in 1944 were Tigers or Panthers. Third, if the German tanks were as deadly as Cooper claims, why did the Germans lose 1,500 tanks in Normandy against about 1,700 Allied tanks? Indeed, Cooper claims that the 3AD lost 648 Shermans in the war, but the division claimed to have destroyed 1,023 German tanks. Clearly, there was no great kill-ratio in the German favor, and the Allies could afford to trade tank-for-tank. Finally, if the Sherman was such a “death trap,” why did the US Army use it later in Korea or the Israelis use it in the 1967 War?
There are a great number of mistakes in this book, beginning with Cooper’s ridiculous claim that General Patton was responsible for delaying the M-26 heavy tank program. Cooper claims that Patton was at a tank demonstration at Tidworth Downs in January 1944 and that, “Patton…insisted that we should downgrade the M26 heavy tank and concentrate on the M4….This turned out to be one of the most disastrous decisions of World War II, and its effect upon the upcoming battle for Western Europe was catastrophic.” Actually, Patton was in Algiers and Italy for most of January 1944, only arriving back in Scotland on 26 January. In fact, it was General McNair of Ground Forces Command, back in the US, who delayed the M-26 program. Cooper sees the M-26 as the panacea for all the US Army’s shortcomings and even claims that the American offensive in November 1944, “would have succeeded if we had had the Pershing” and the resulting American breakthrough could have forestalled the Ardennes offensive and “the war could have ended five months earlier.” This is just sheer nonsense and ignores the logistical and weather problems that doomed that offensive.
Cooper continually discusses events he did not witness and in fact, only about one-third of the book covers his own experiences. Instead of discussing maintenance operations in detail, Cooper opines about everything from U-Boats, to V-2 rockets, to strategic bombing, to the July 20th Plot. He falsely states that, “the British had secured a model of the German enigma decoding machine and were using it to decode German messages.” Cooper writes, “not until July 25, the night before the Saint-Lo breakthrough, was Rommel able to secure the release of the panzer divisions in reserve in the Pas de Clais area.” Actually, Rommel was wounded on 17 July and in a hospital on July 25th. In another chapter, Cooper writes that, “the British had bombed the city [Darmstadt] during a night raid in February,” and “more than 40,000 died in this inferno.” Actually, the RAF bombed Darmstadt on 11 September 1944, killing about 12,000. Dresden was bombed on 13 February 1945, killing about 40,000. Obviously, the author has confused cities and raids.
Even where Cooper is dealing with issues closer to his own experience, he tends to exaggerate or deliver incorrect information. He describes the VII Corps as an “armor corps,” but it was not. Cooper’s description of a counterattack by the German Panzer Lehr division is totally inaccurate; he states that, “July 11 became one of the most critical in the battle of Normandy. The Germans launched a massive counterattack along the Saint-Lo- Saint Jean de Daye highway…” In fact, one under strength German division attacked three US divisions. The Americans lost only 100 casualties, while the Germans suffered 25% armor losses. The Official history calls this attack “a dismal and costly failure.” Cooper wrote that, “Combat Command A…put up a terrific defense in the vicinity of Saint Jean de Daye…” but actually it was CCB, since CCA in reserve. On another occasion, Cooper claims that his unit received the 60,000th Sherman produced, but official records indicate that only 49,234 of all models were built. Cooper claims that the 3rd Armored Division had 17,000 soldiers, but the authorized strength was about 14,500. Can’t this guy remember anything correctly?
Cooper’s description of the death of MGN Rose is virtually plagiarized from the official history and a number of articles in ARMOR magazine in the past decade reveal that Rose was an extreme risk-taker. Reading “Death Traps,” the uninitiated may actually believe that the US Army was badly defeated in Europe. Cooper even claims that, as the 3rd Armored Division approached the Elbe River in the last days of the war that, “with our division spread out and opposed by three new divisions, our situation was critical.” If anybody’s situation was critical in April 1945, it was Germany’s. Actually, the 3rd Armored Division had one key weakness not noted by Cooper, namely the shortage of infantry. The division had a poor ratio of 2:1 between tanks and infantry, and this deficiency often required the 3AD to borrow an infantry RCT from other units. While the much-maligned Sherman tank was far from perfect, it did the job it was designed for, a fact that is missed by this author.
Here is the Chieftains take.: The important part: Death Traps is not a reliable source. Don’t cite it. Or the History Channel show based on it.
My opinion on the book is that it is both a bad book from a historical perspective and writing perspective since it’s a hard book to read. Most of the book is just boring. Belton Cooper had a tough job, but it was also not very entertaining, and he didn’t focus on the aspects of his job that could have been. He focuses on a lot of personal speculation presented as fact, and the truly interesting things like his experiences with the M26 Pershing, and the Super Pershing are not covered in great detail. This book isn’t worth it unless it’s one of those penny plus shipping deals, and even then read it was a large grain of salt.