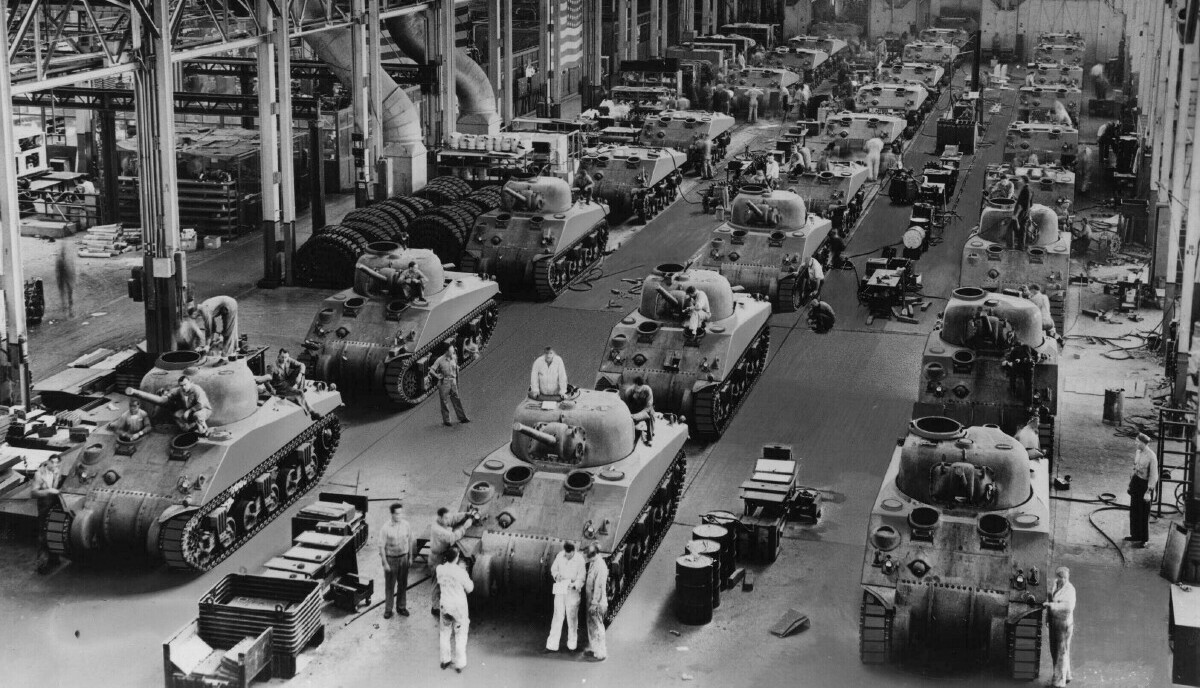
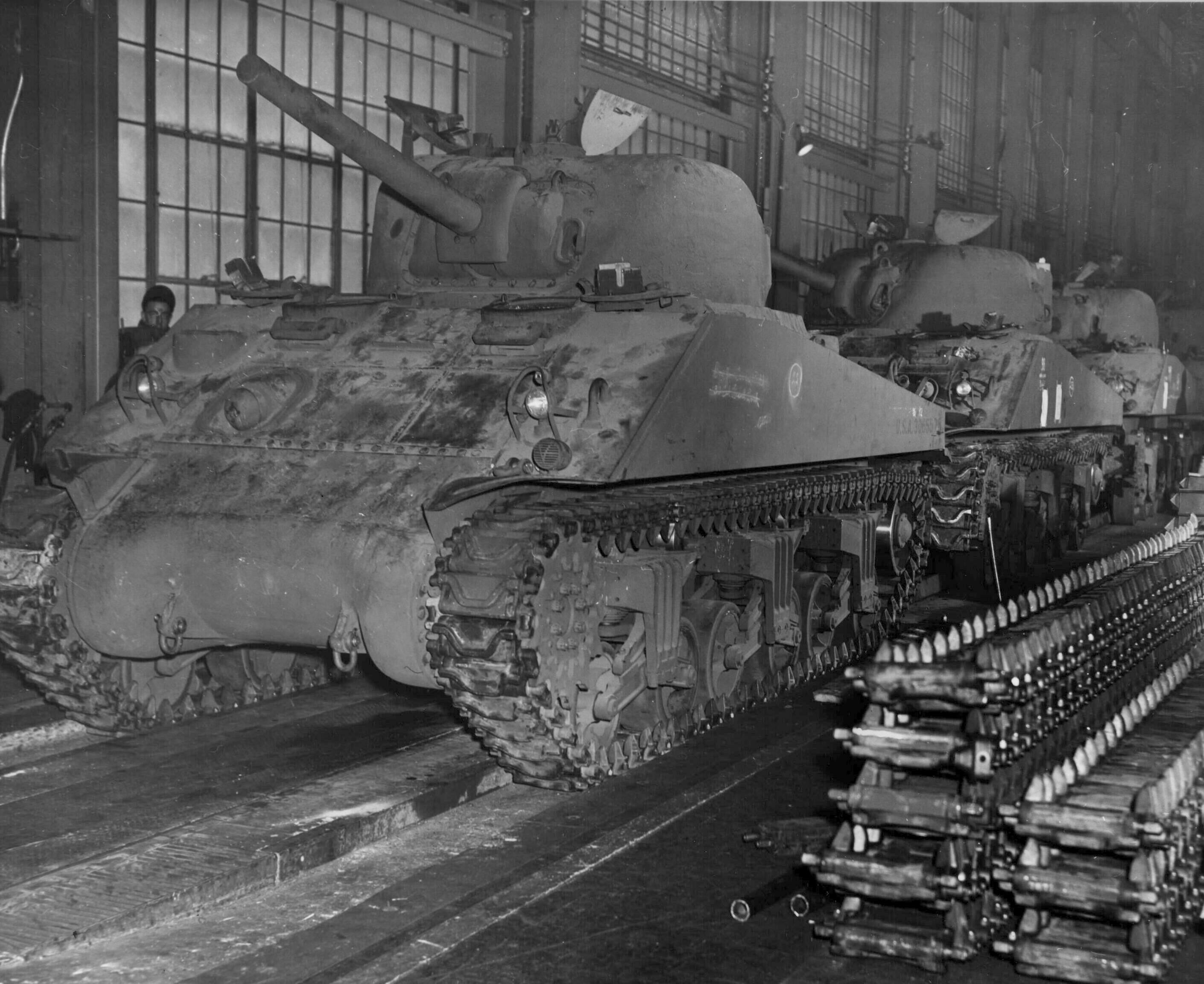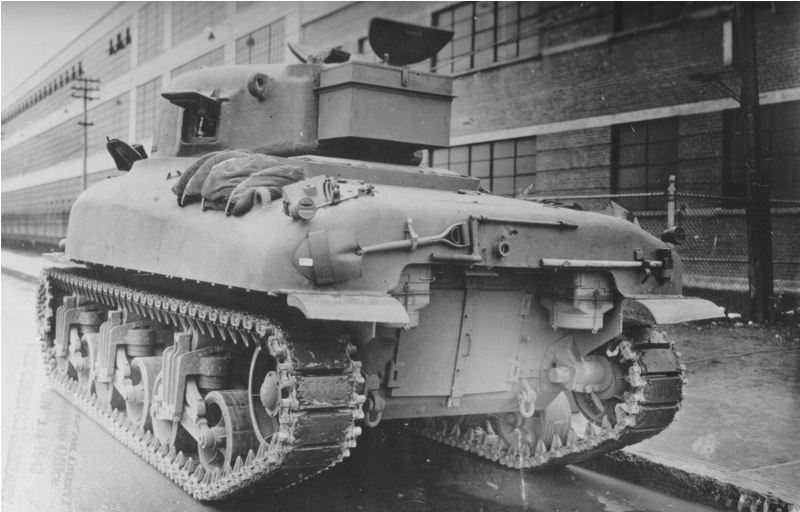
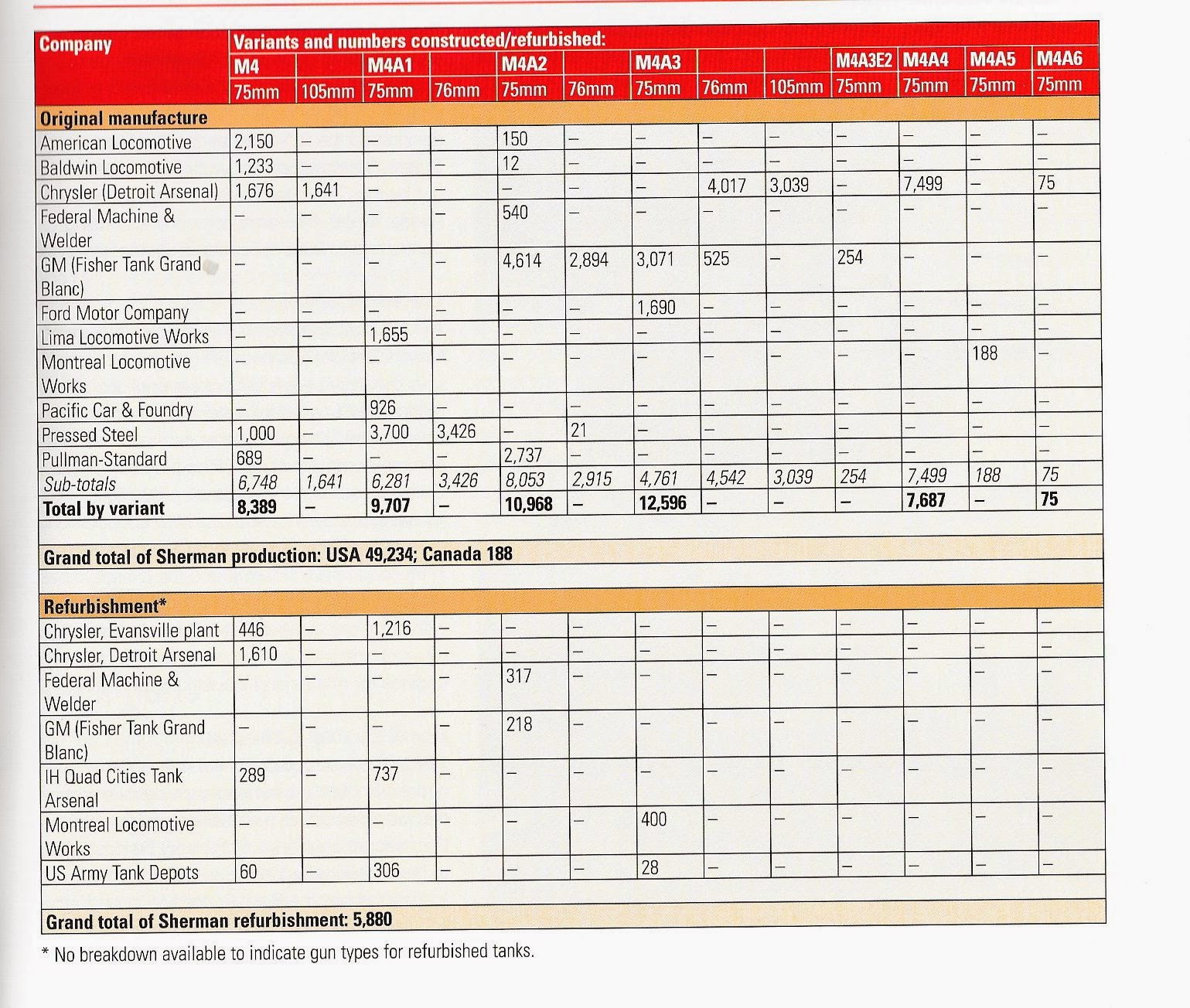
Sherman Builders: They Had 10 and 1 in Canada.
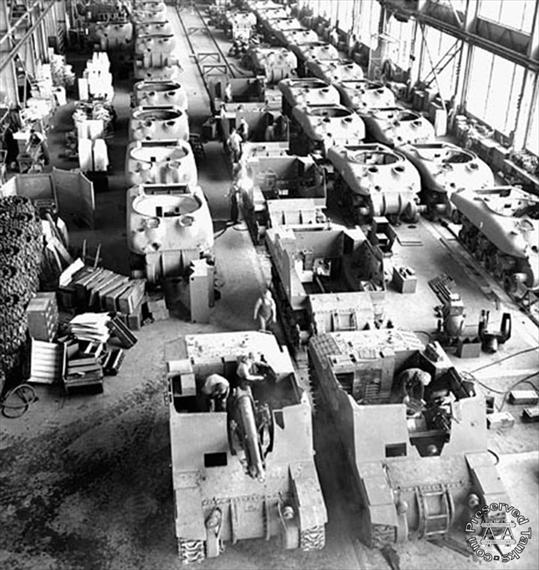
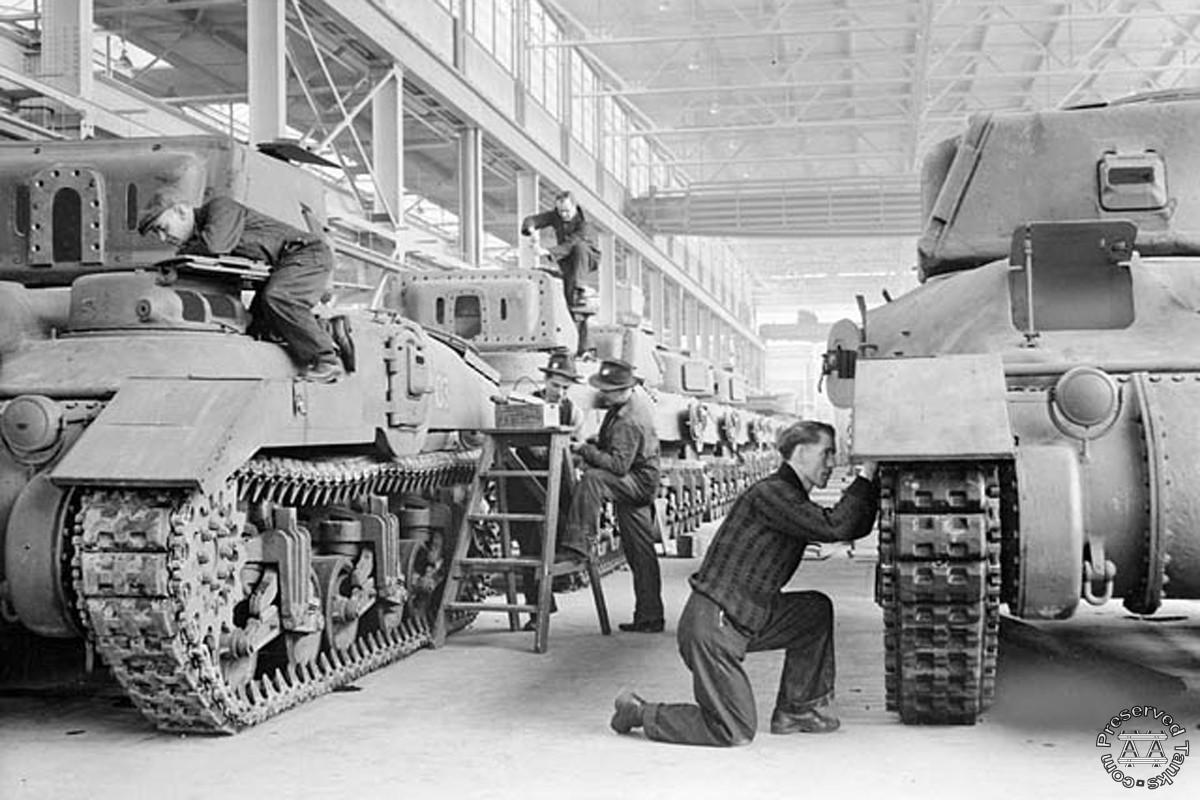
Most of the information in this section will be a summation of the section from the book Son of a Sherman. Other stuff I had to dig around on the internet for. Anyone who has more info on the tank makers, please feel free to contact me. Parts from all these tank makers would interchange. Many used the same subcontractors. I don’t think anyone has tried or if it’s even possible to track down all the sub-contractors who contributed parts to the Sherman at this point. Some of the manufacturers were more successful than others, some only producing a fraction of the total Sherman production, others producing large percentages. By the end of production, all the US and her allies ‘ needs for Shermans were being handled by just three of these factories.
American Locomotive (ALCO)
ALCO also produced M3 and M3A1 Lees and made Shermans up to 1943. They were a fairly successful pre-war locomotive manufacturer founded in 1901 in Schenectady, New York. They also owned Montreal Locomotive Works. ALCO made several versions of the Sherman, and stayed in the tank game until the late 50s, helping with M47 and M48 production. The company went under in 1969.
Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLM)
Baldwin was another early producer, building three versions of the Lee, The M3A2, M3A3, and M3A5. They mostly built small hatch M4s, with just a handful of M4A2(12). They were out of the Sherman game by 1944 and out of business by 72. They were founded in Philly in 1825 and produced 70,000 steam locomotives before they died.
Chrysler Defense Arsenal (CDA)
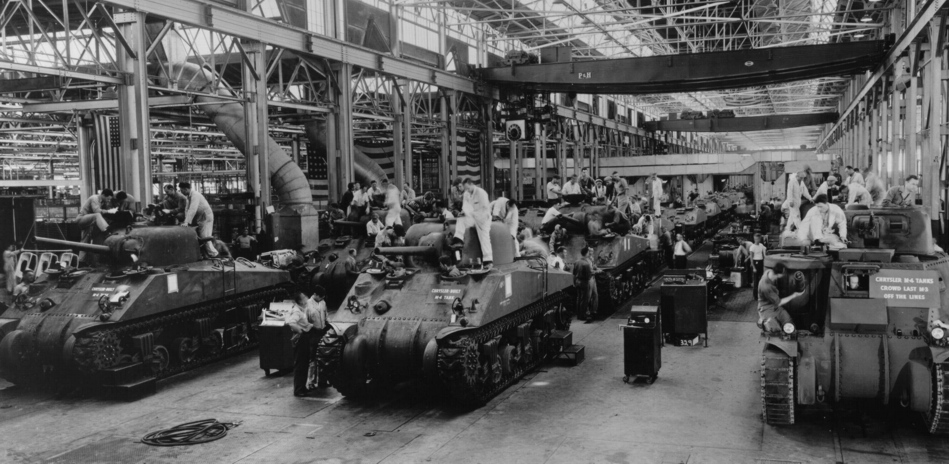

Chrysler Defense Arsenal is kind of special. It was a purpose-built tank factory, funded by the US Government, and managed and built by Chrysler. Construction of the factory started in September of 1940. Completed M3 Lee tanks were rolling off the line by April of 1941. This was before the factory was even finished being built. It was built to stand up to aerial bombing. They produced M4A4, and M4 tanks as well and M4 105s, M4A3(105)s, and M4A3 76 tank and nearly 18,000 of them. Chrysler was the sole producer of M4A3E8 76 w Shermans, or the tank commonly known and the Easy 8. They produced 2617 units, but post-war many A3 76 tanks were converted over to HVSS suspension. A very big chunk of the overall Sherman production came from this factory and it went on to produce M26 Pershing tanks.
Chrysler built this factory in a suburb of Detroit, Warren Township Michigan. Chrysler used its many other facilities in the Detroit area as sub manufacturers, and many of their sub-contractors got involved too. CDA not only produced the tanks, it also had the capacity to pump out huge numbers of spare parts. CDA lived into the 90s before Chrysler Defense Systems got sold off to General Dynamics. It took part in making the M26, M46, M47, M48, M60, and M1 tanks.
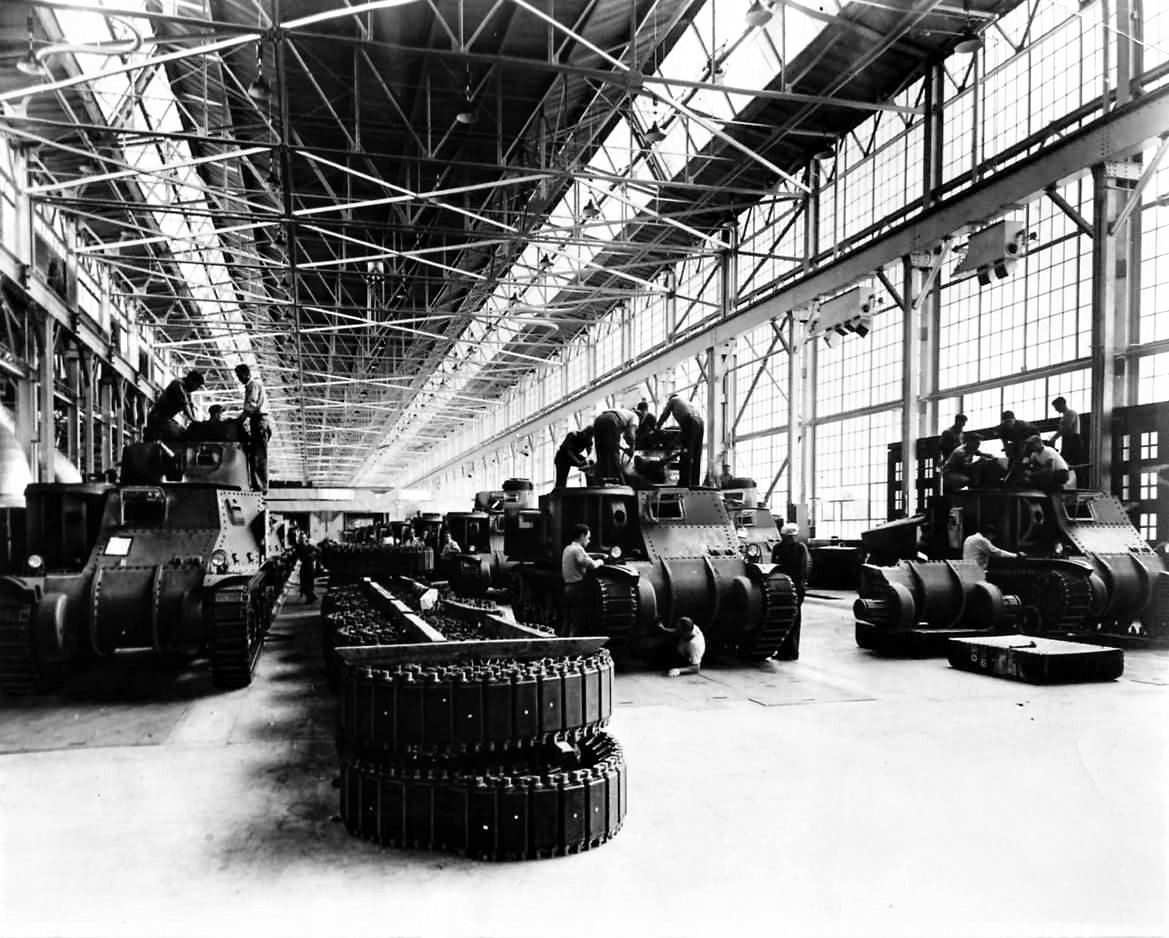
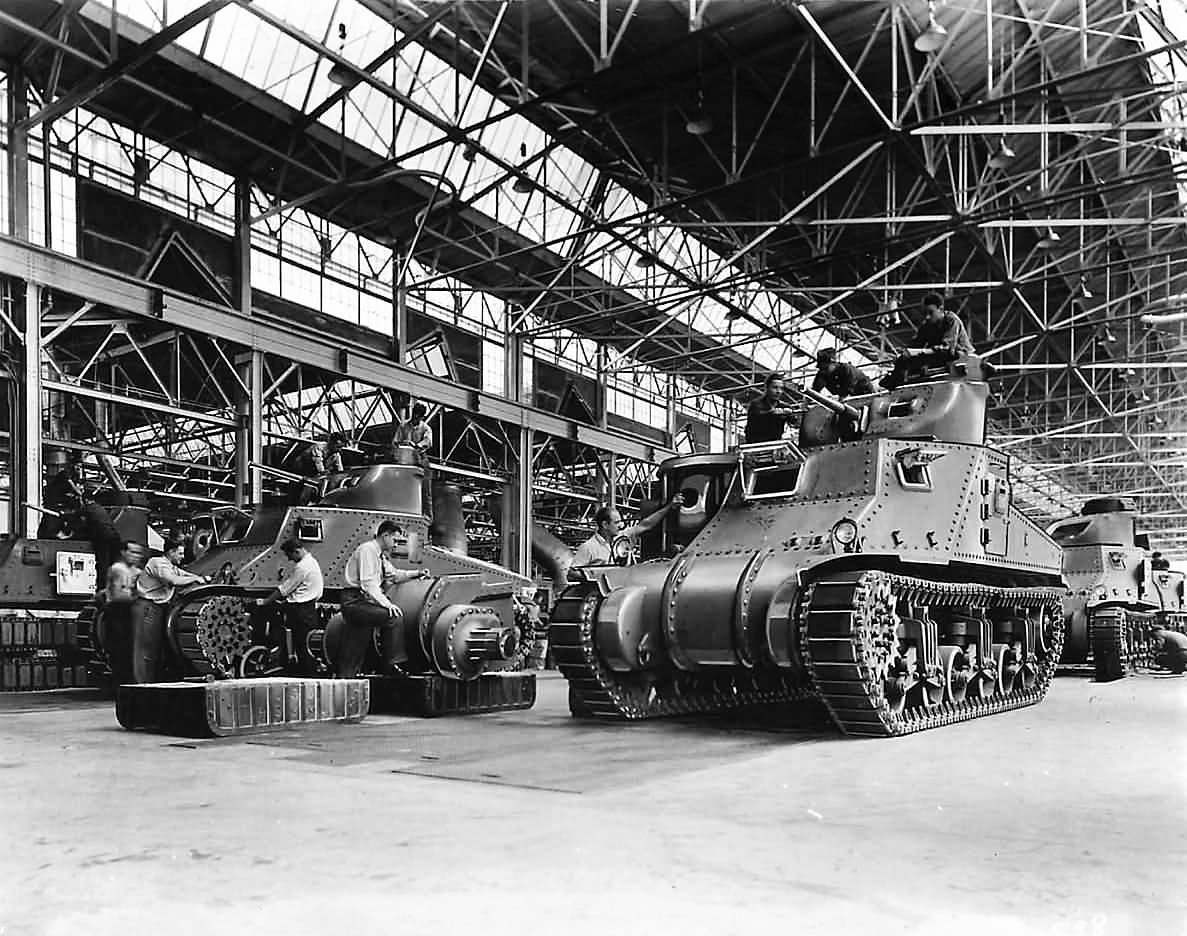
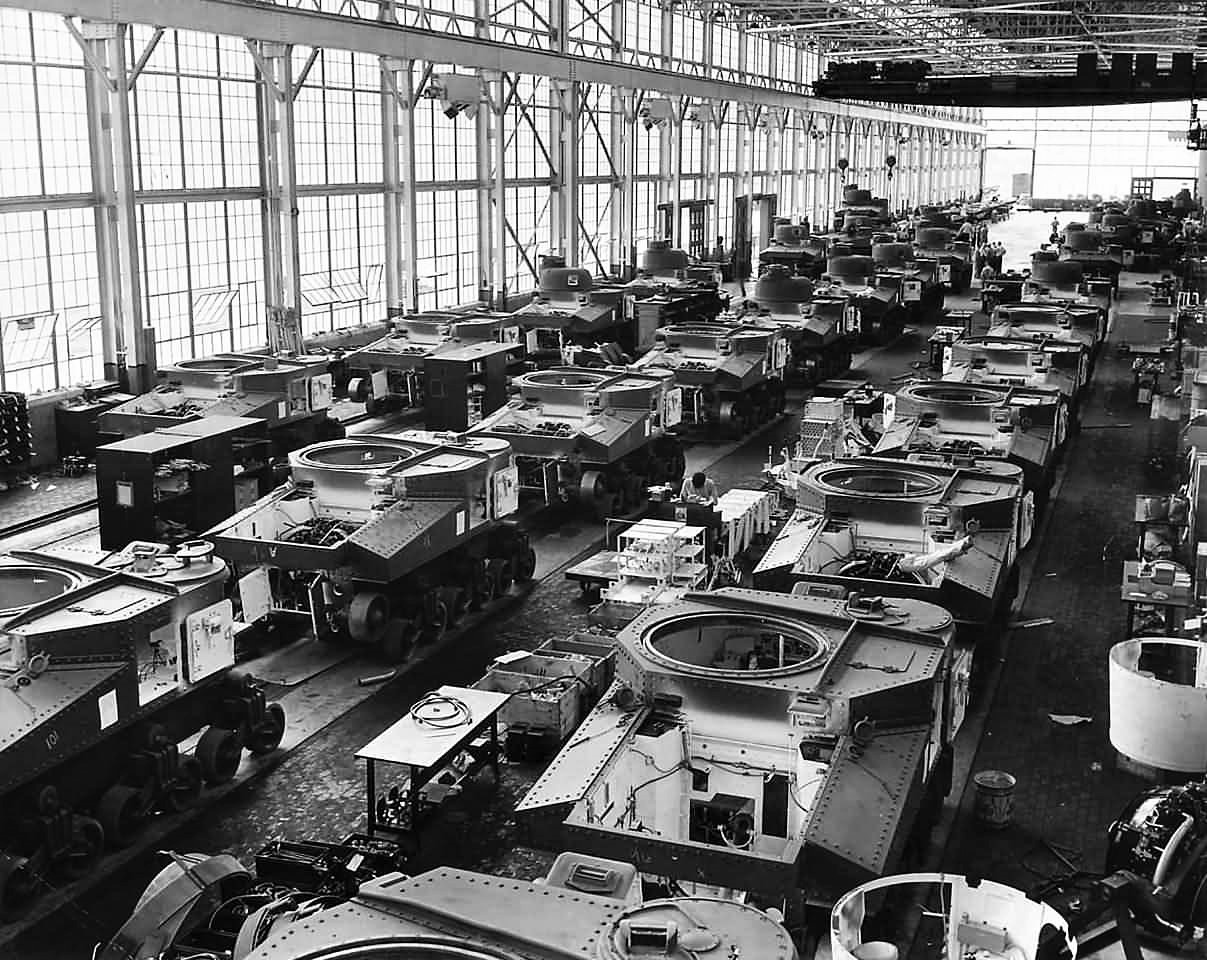



Federal Machine & Welder (FMW)
I couldn’t find much out about FMW, Son of a Sherman says they were founded in Warren Ohio in 1917. They produced less than a thousand M4A2 small hatch tanks. They were slow to produce them, making about 50 a month. They were not contracted to make any more Shermans after their first 540 total, 1942 contract. They did build some M7 GMCs and M32 tank retrievers. They were out of business by the mid-fifties.
Fisher Tank Arsenal (FTA)
Fisher Tanks Arsenal (FTA) has a lot of common with Chrysler Defense Arsenal, except this time Uncle Sam went to Fisher Body, a division of General Motors. Fisher decided to build the tank plant in Grand Blanc, south of Flint Michigan. The factory broke ground in November of 1941 and the first M4A2 Sherman rolled off the line in January of 1942 before the factory was fully built.
The M4A2 was something of this factory specialty, in particular early on, with them producing a large number of the small hatch M4A2 sent off to Russia, and a few of the rarer large hatch 75mm gun tanks, around 986 small hatch tanks, and about 286 large hatch tanks.
They also produced nearly 1600 large hatch, 76mm gun tanks, or the M4A2 (76)w. These tanks went exclusively to Russia as part of Lend-Lease. These tanks were ordered over four different contracts and the final ones off the production line were all HVSS tanks. The HVSS suspension may have seen combat with the Russians before the US Army used it. Oddly, this factory also produced M4A3 76w tanks, but never with the HVSS suspension. Fisher produced a significant number of M4A3 and Large hatch 75mm tanks at their factory, but nowhere near their M4A2 production.
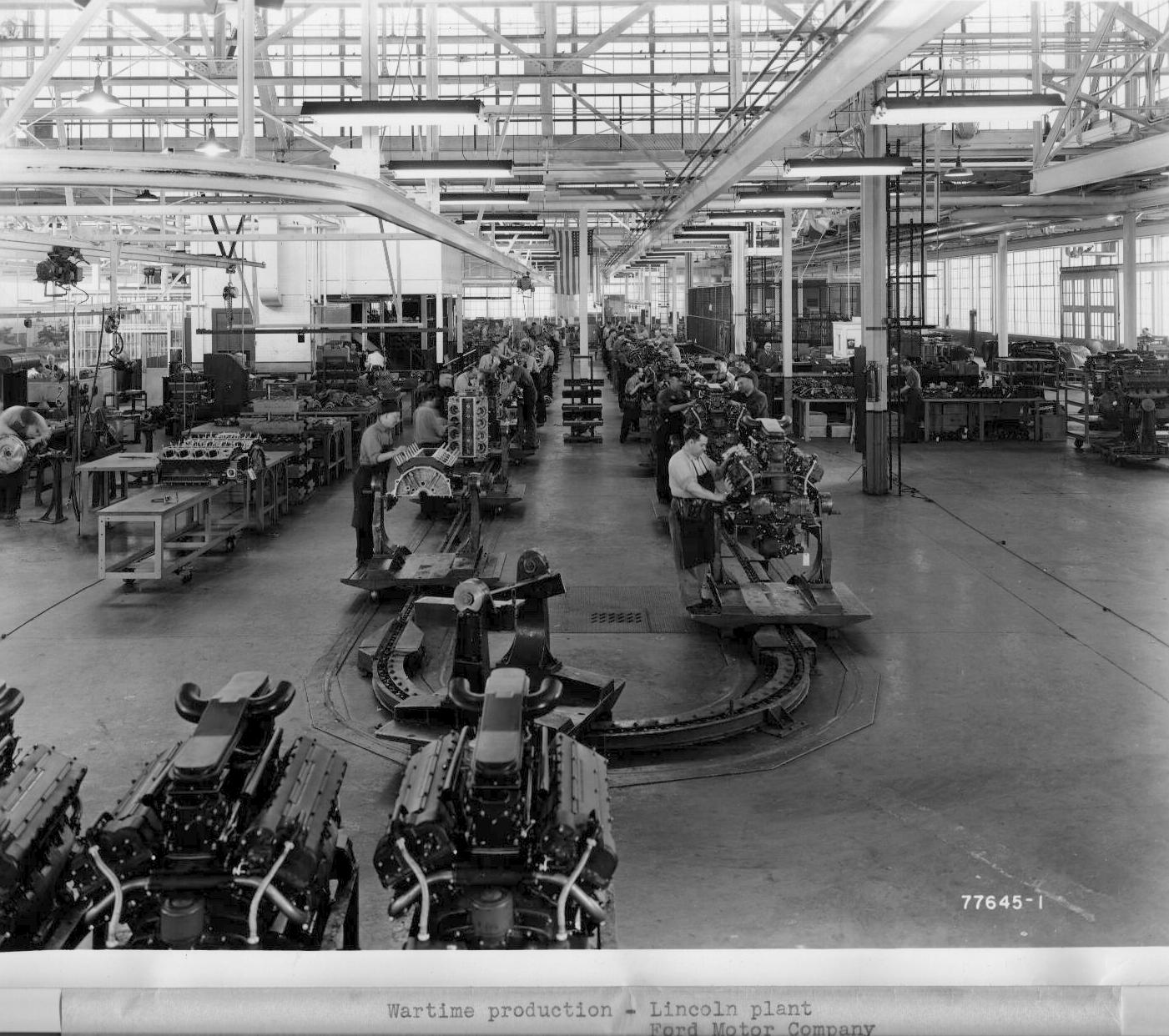
Ford Motor Company (FMC)
Ford was a surprisingly small player in the Sherman tale. They are very important in that they developed the Ford GAA V8 covered earlier, and a lot of spare parts. But they only produced 1690 small hatch Shermans between June of 42 and Oct 43. They built a few M10s as well. All these tanks and tank destroyers were produced at their Highland Park facility. After 1943, they stopped building tanks, and wouldn’t get back into until the 50s, and even then it was just for a large production run over a short time, of M48s.
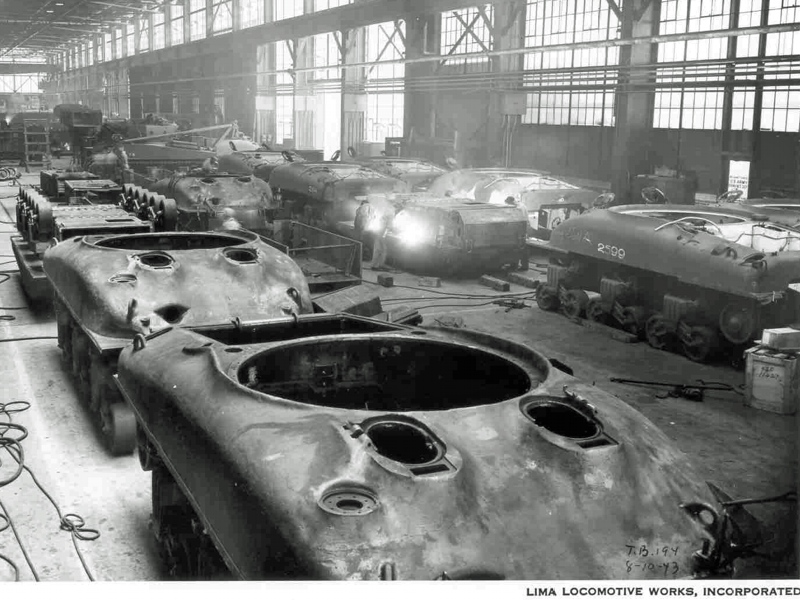
Lima Locomotive Works (LLW)
Lima was one of the first producers of the cast hull M4A1. It did not produce any Lee tanks. Its production capacity had been taken by locomotives to the point just before Sherman production started. They produced the first production M4A1, that was shipped to England, named ‘Michael’, and it’s still on display at the Bovington Museum. They produced Shermans from February of 42 to September of 1943, producing M4A1s exclusively, and they built 1655 tanks. The war was a boon for Lima, they’d been in business since 1870, and the contracts from the military for locomotives really helped them out. Postwar, they failed to successfully convert to diesel-electric locomotives and merged with another firm.
Montreal Locomotive Works (MCW)
MLW was owned by American Locomotive. They produced some wacky Canadian tank based on the Lee chassis, called the Ram, and Ram II, these floppy creations were only armed with a 2 pounder in the Rams case, and a 6 pounder, in the Ram IIs case, and they produced almost 2000 of the wacky things, what’s that all aboot? They eventually got around to producing a proper Sherman tank, the M4A1 “Grizzly”, producing only about 188 tanks. A very few had an all-metal track system that required a different sprocket. Other than that, there was no difference between a grizzly and an M4A1 manufactured by any other Sherman builder. Don’t believe the Canadian propaganda about it having thicker armor!
Pacific Car & Foundry (PCF)
PCF was founded in 1905 in Bellevue, Washington. After they bought out their only real competitor in the early 20s, they were the only heavy machinery company and foundry in the Pacific Northwest. They were the go-to foundry for steel used in the building of many Seattle landmarks. In 1924 the founder, William Pigott sold a controlling interest in the company to American Car and Foundry Company. In most stories about a company, it would end right there, but in a twist of fate, the Son of William Pigott, Paul Pigott, bought back a controlling share of the company in 1934.
At first, the company seemed to do ok during the great depression, but it was really on the ropes until just before WWII, when the increase in military spending helped them out. Their steel and aluminum were used in the B17, numerous Naval vessels, and tanks. They were also one of the Sherman tank producers that could make their own M34 Gun Mounts. They produced enough other Sherman factories used theirs too.
The only west coast tank maker, PCF produced 926 M4A1s from May of 1942 to November of 1943. The foundry had the facilities to produce all the big casting, the M4A1 Sherman used, in-house. As soon as production stopped they started production on the M26 tractor, the truck portion of the M26 tank transporter, also known as the Dragon Wagon. They never got back into tank production again, but they did produce one very special tank destroyer. The almost mythical T28 super heavy tank and the army managed to lose one.
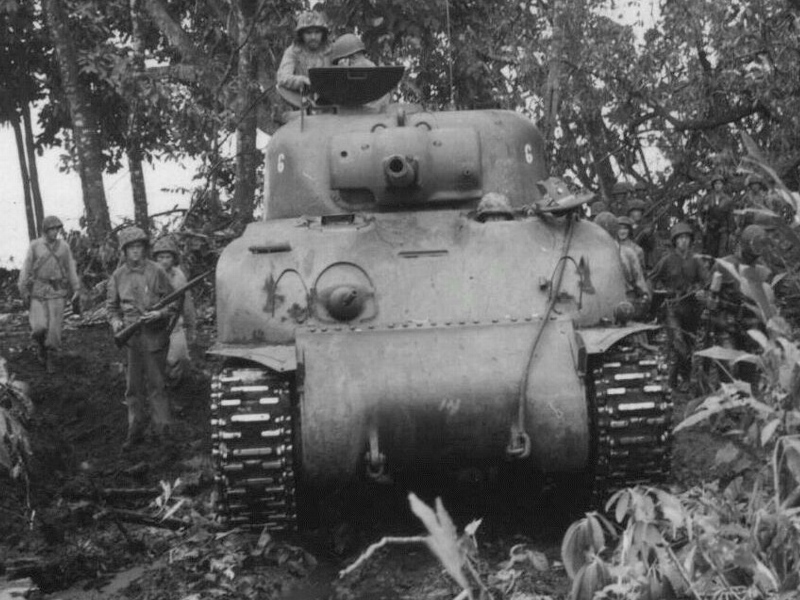
The Shermans they produced were used by units training up and down the west coast, and many were sent to the Pacific. Company A, of the 1st Marine tank battalion, received a 24 of PCF’s M4A1 Shermans, the only ones the Marines would use. These PCF Shermans have a few things that make them easier to identify, the easiest to see is the dust cover mount around the hull machine gun, PCF’s is distinct and made from a strip of steel instead of a rod. Many of these Shermans were produced with the T49 steel tracks. These tanks would see combat in the swamps and jungles of Cape Gloucester. A battle I will cover in detail later.
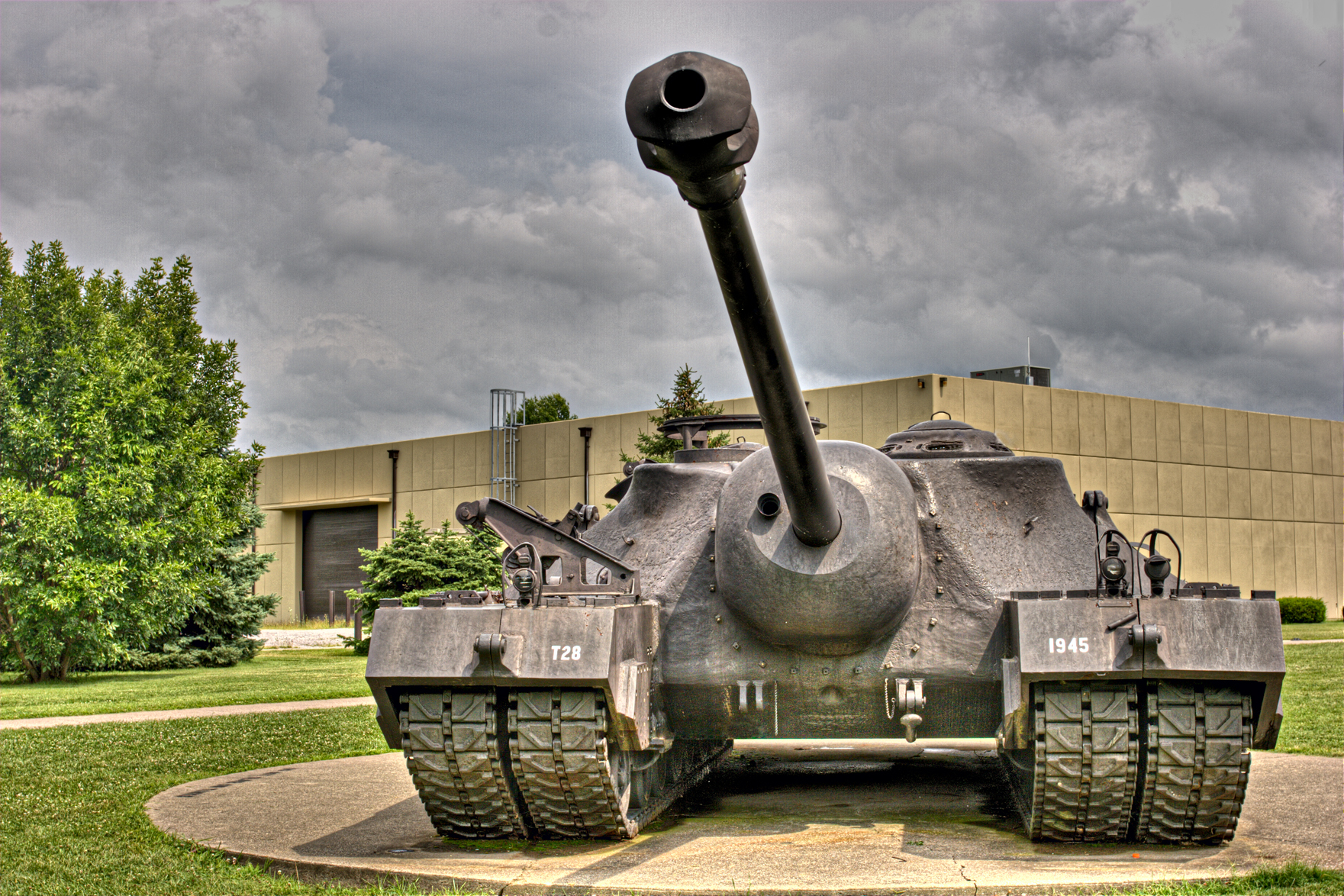


The T28, also known as the T95 105mm gun motor carriage, two of these massive vehicles were made, and PCF made both. They came in at 100 just under 100 tons and were designed to get a very powerful 105mm gun close enough to knock out heavy fortifications, like the type along the Siegfried line. It was also considered for use in the Invasion of Japan had that been necessary, and man, think of the weird porn the Japanese would come up with if we had invaded with a bunch of these bad boys, instead of nuking them. It had a set of double wide HVSS suspension on each side, with four bogie groups, and armor up to a foot thick. It had a four-man crew and used the same 500 horsepower Ford GAA V8 to move it. Yes, 100 tons, 500HP, a real hot rod that thing was. Development ceased after the war, and any kind of testing on the two prototypes stopped by 47. One prototype burned out, and was scrapped; the other just disappeared for several decades and was found in a remote spot on Fort Belvoir in Virginia. It is now stored in an army parking lot, not open to the public, rusting away.
Pacific Car & Foundry still exist today as PACCAR Inc., one of the largest truck makers in the world. They own both Kenworth and Peterbilt. They also produced much of the steel structure on the Twin towers of the World Trade Center. They built the PACCAR tower in Bellevue in in the late 60s and it’s still their HQ today. They are worth 18,8 billion as of 2013.
Pressed Steel Car (PST)
PSC was one of the big boys of Sherman production, and they also produced the final M4s made, a group of 30 M4A1 76 HVSS tanks. PSC was founded in Pittsburg in 1899, but their tank factory was in Joliet, Illinois. They were the second manufacturer to make the tank and across all the versions they made, they produced 8147 Sherman tanks.
They started tank production with the M3 Lee in June of 41 and stopped production on that in August of 1942. They then produced the M4A1 from March of 42 to December of 43, and the standard M4 from October of 42 to August of 43.
They were one of the final three tank makers to stay in the tank making business after 1943, along with CDA and FTA. PSC would produce large hatch M4A1 76 tanks, including HVSS models late in the run, totaling more than 3400 M4A1 tanks. They produced 21, M4A2 76 HVSS tanks, towards the end of 45.
They were out of business by 56, with no tank production after those final 30 M4A1 76 HVSS tanks.
Pullman Standard (PSCC)
Pullman Standard was a pretty famous luxury train passenger car maker and another company that made rolling stock combined into one company. Pullman Palace Car Co was founded in 1867, or thereabouts. I’m sure some train geek will be dying to fill me in on the company’s history but I’m not really going to look deeply into it. It does make for one of the more interesting stories about a Sherman tank producer. Their main tank factory was in Butler, Pennsylvania. And they helped produce some Grant tanks before they started Sherman production.
They produced the M4A2 from April of 42 to September of 43 and produced 2737 tanks. They also produced 689 standard M4 Sherman tanks from May of 43 to September of 43. Soon after these contracts were finished the US Government broke the company up due to some anti-trust complaint.
…
The thing to remember about all the Sherman makers is each one had a small imprint on the tanks they produced. So, yes, an M4A1 small hatch tank was the same no matter who made it and all parts would interchange with no modification needed, but the tanks from different makers still had small, cosmetic differences. They may have been something like nonstandard hinges on the rear engine doors to the use of built-up antenna mounts instead of cast. Or wide drivers hoods or narrow, to where the lift rings on the hull were and how they were made or even Chrysler’s unique drive sprocket they put on all their post A4 tanks. None of this meant the parts couldn’t be salvaged and used on another Sherman from another factory without much trouble. Some factories may have produced tanks faster than others, but they all produced them within the specification of the contract or they were not accepted.

Sources: Sherman by Hunnicutt, Son of a Sherman by Stansell and Laughlin, Tanks are a Mighty Fine Thing by Stout, various company websites











