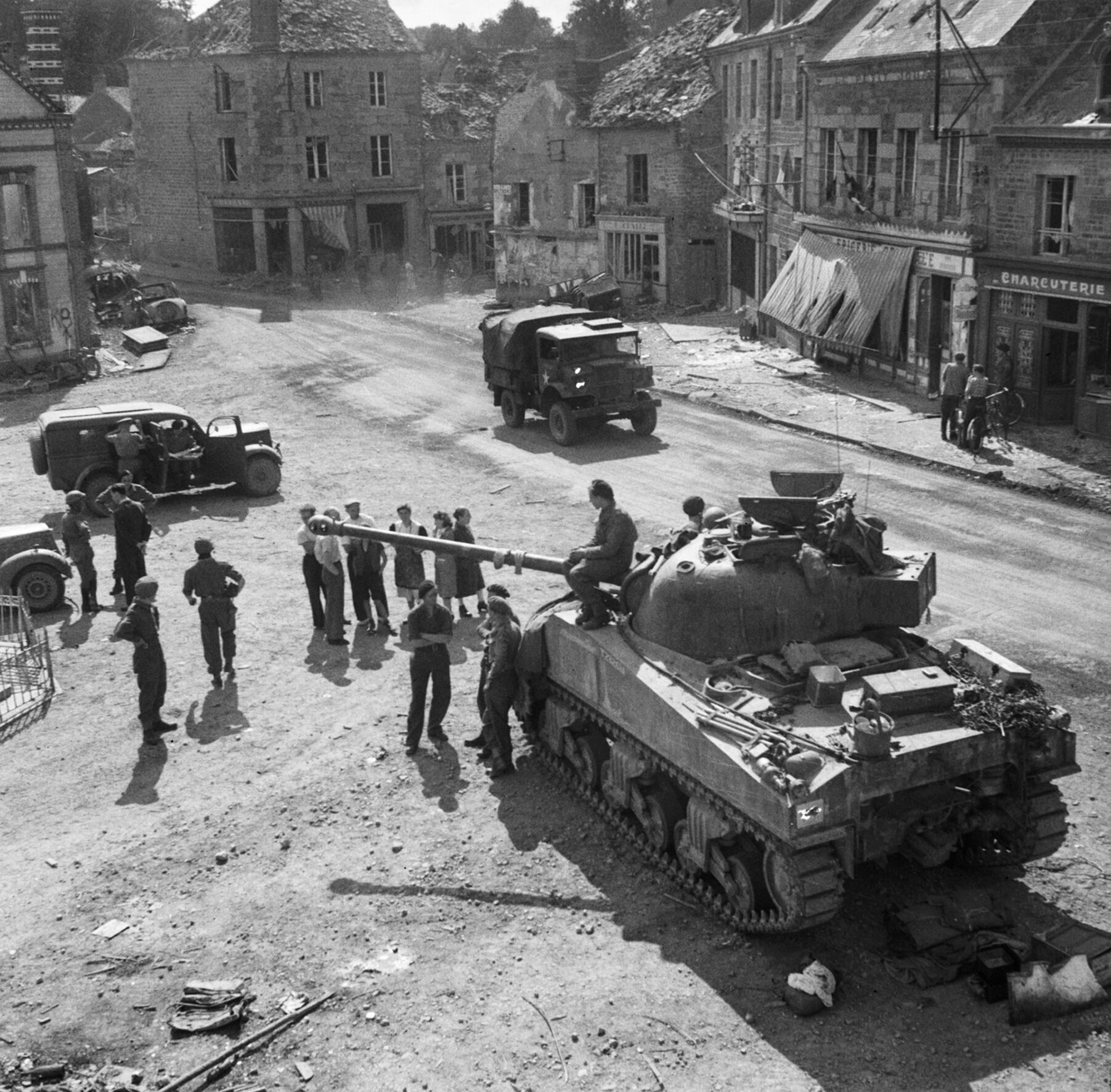
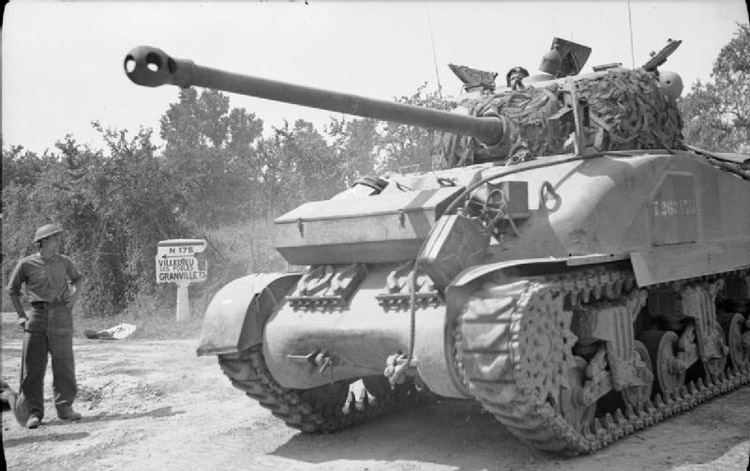
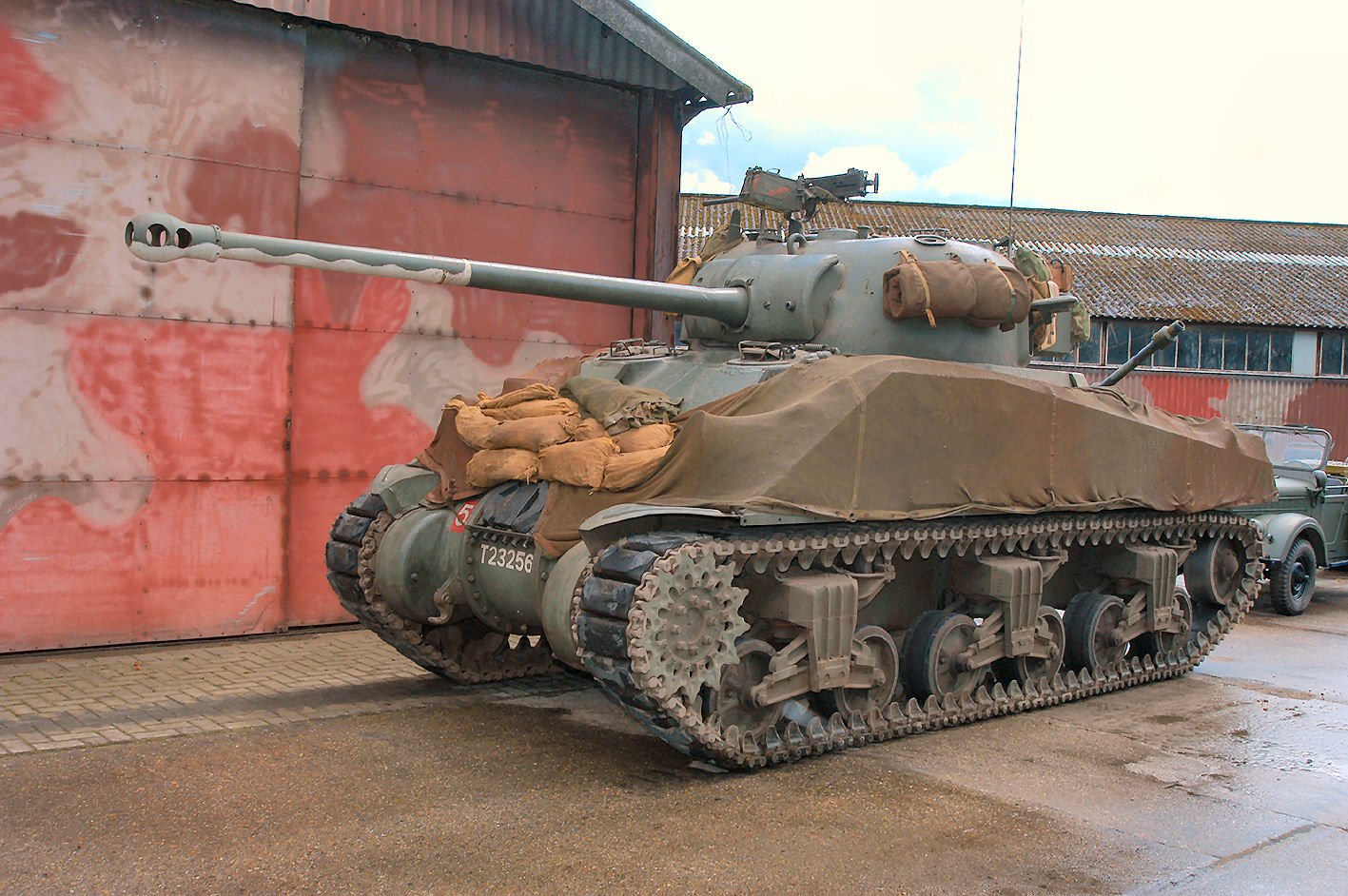
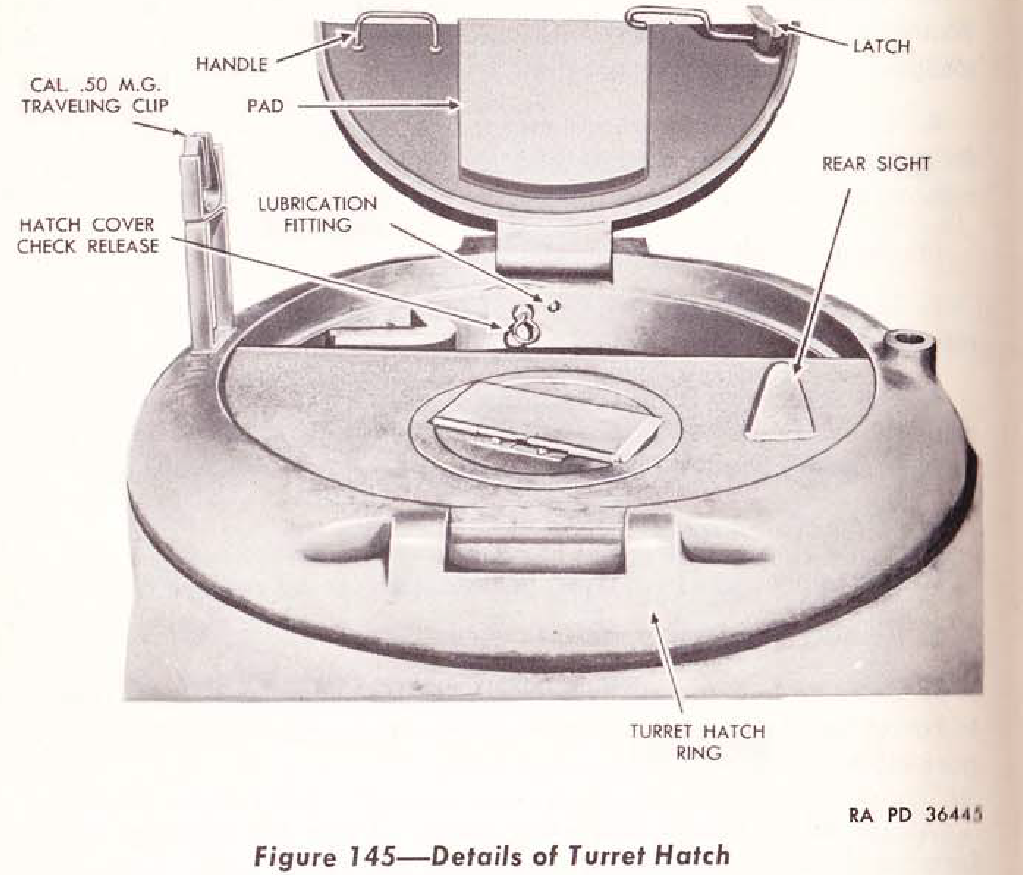
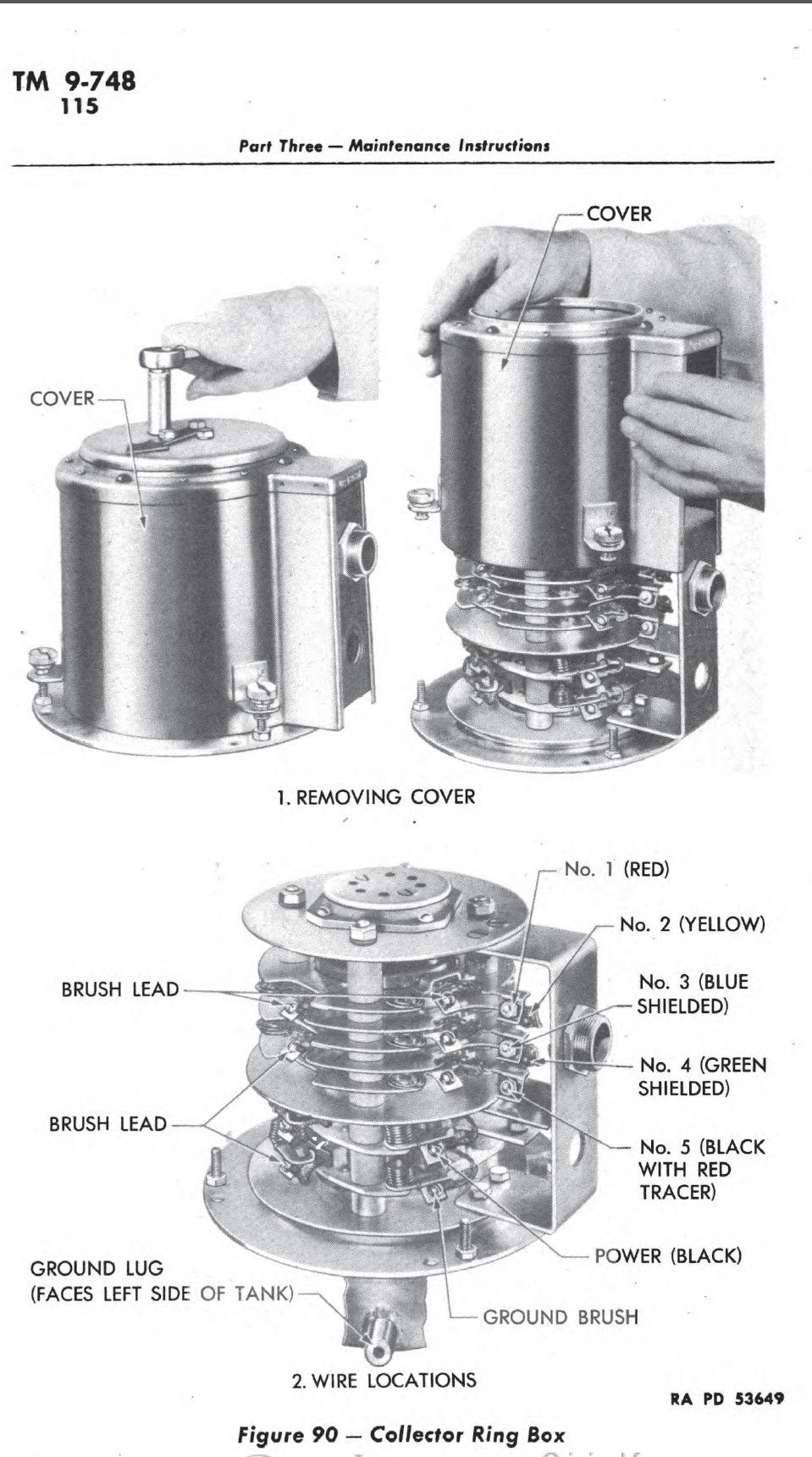
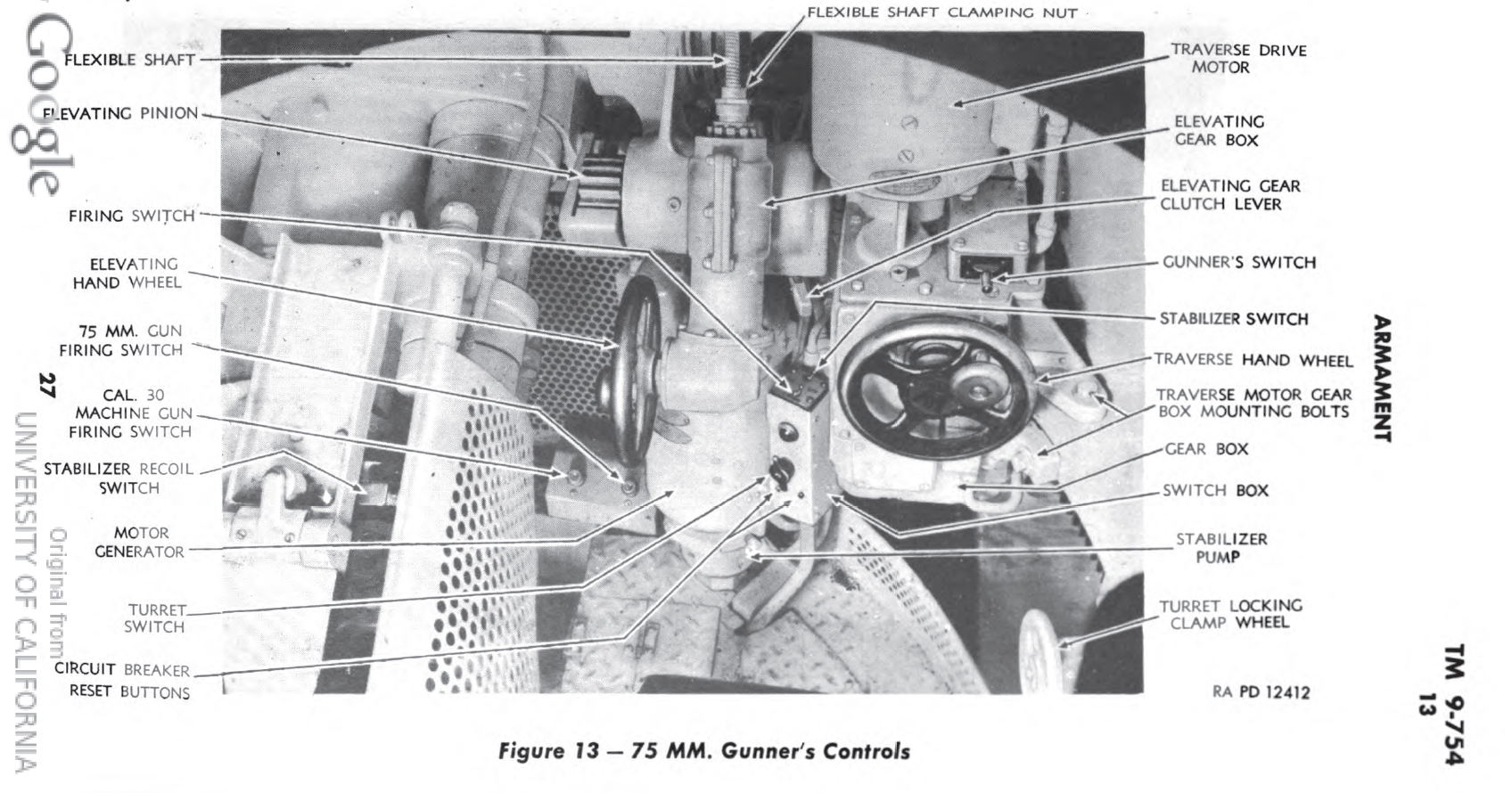
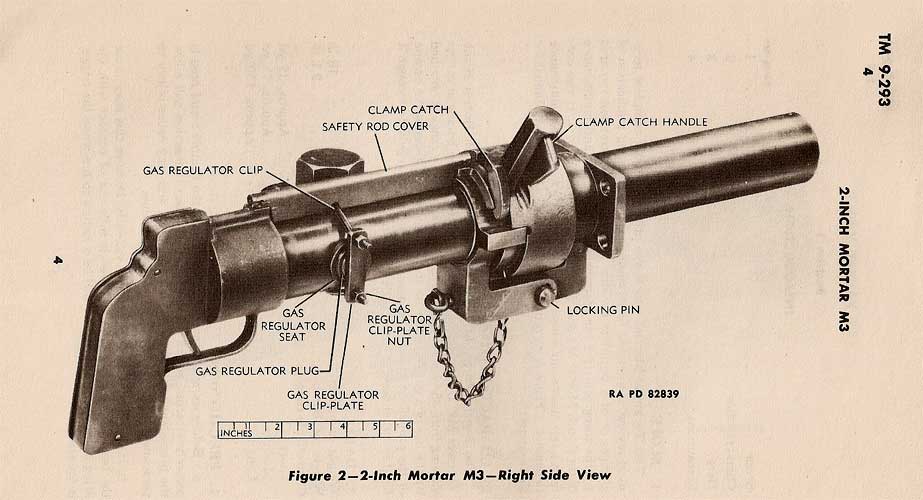
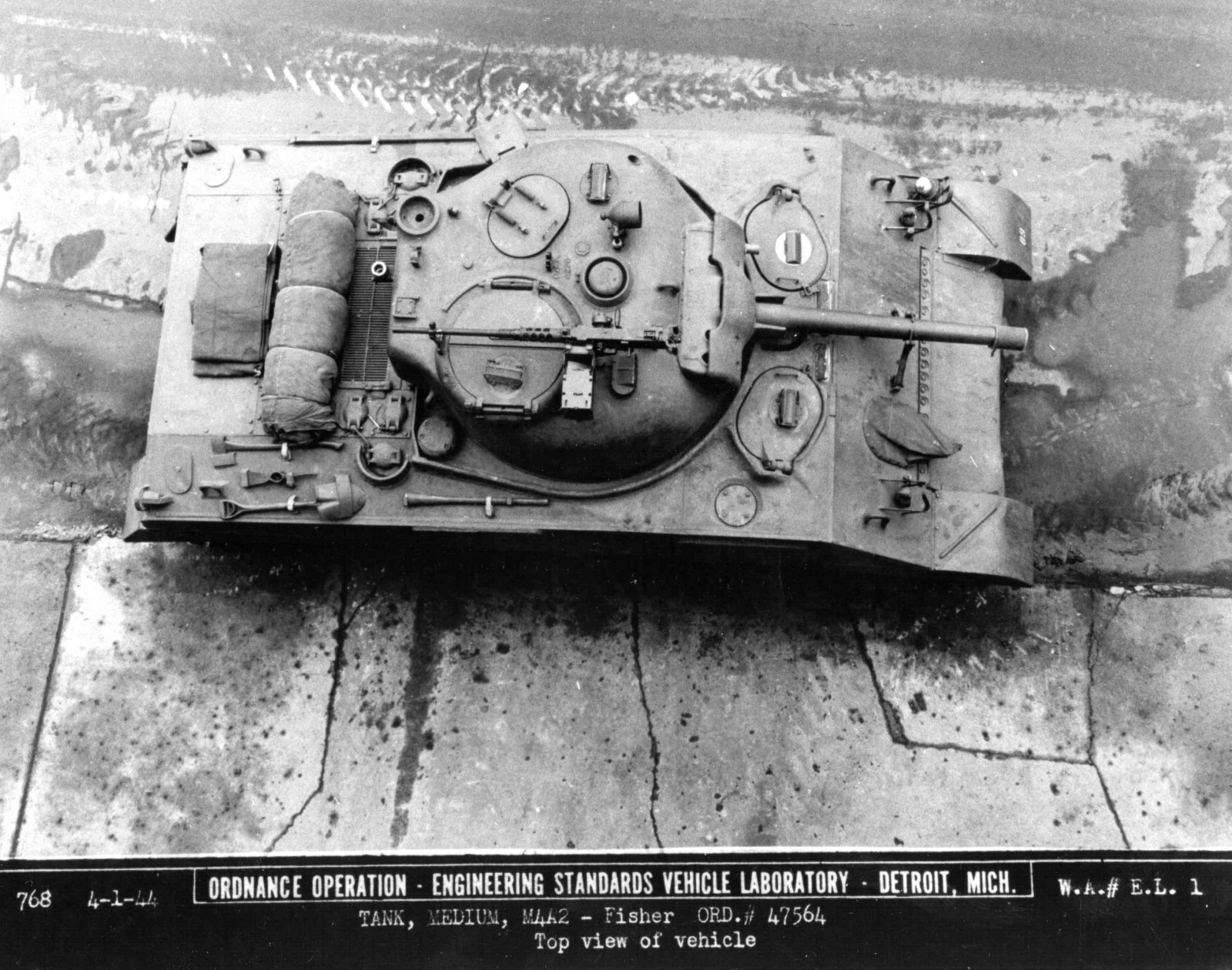
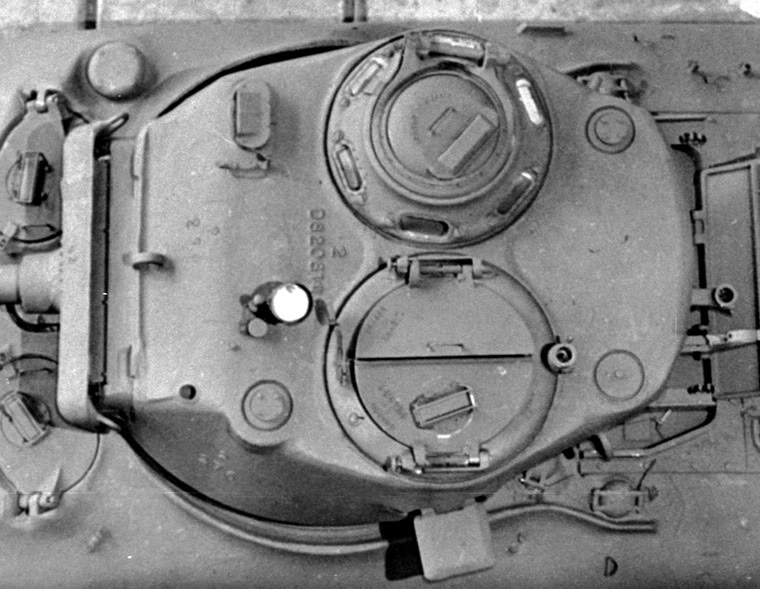
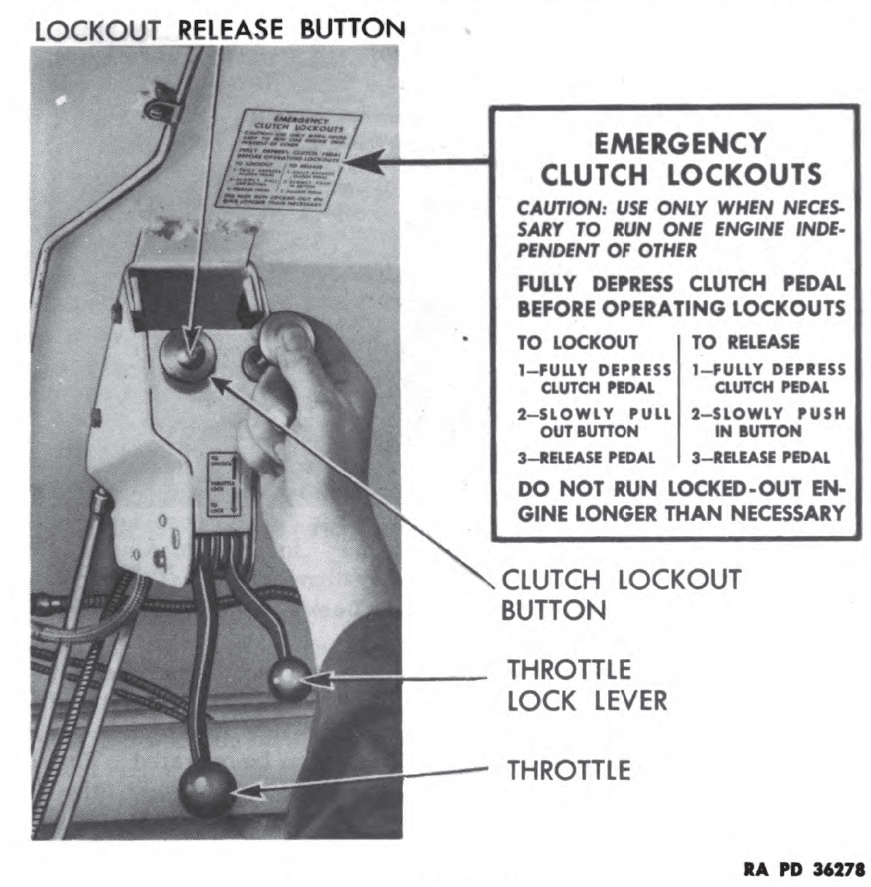
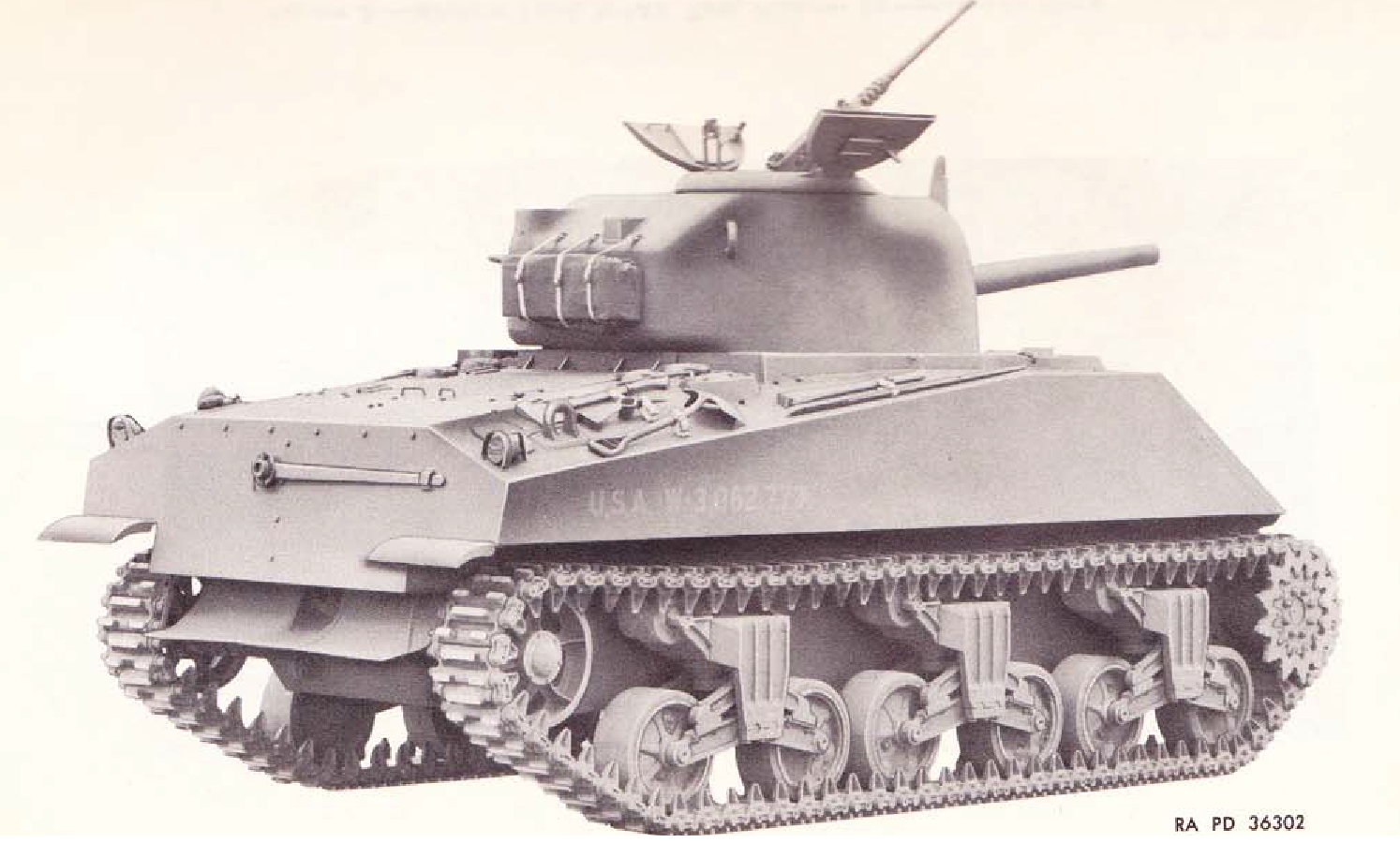
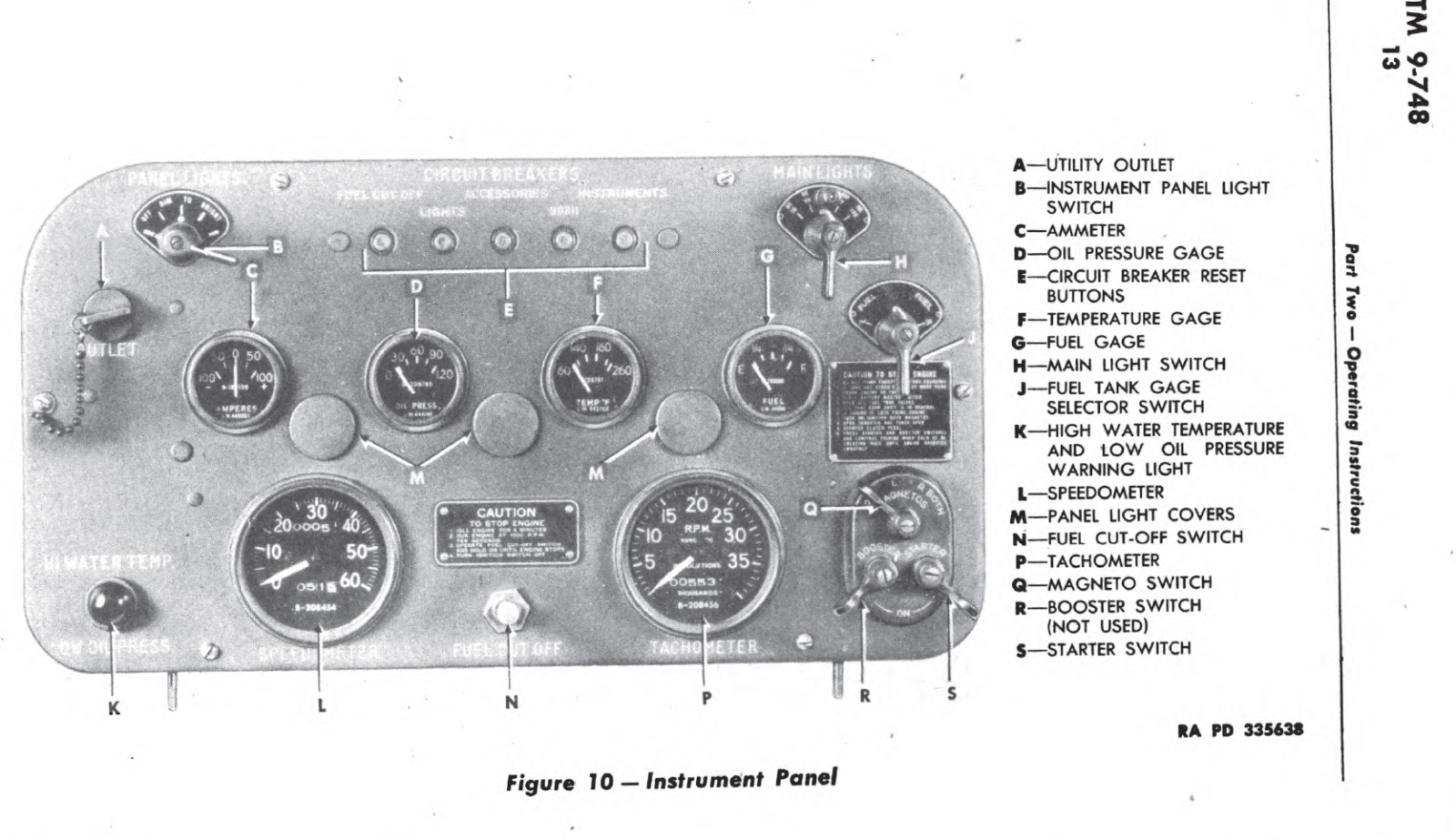
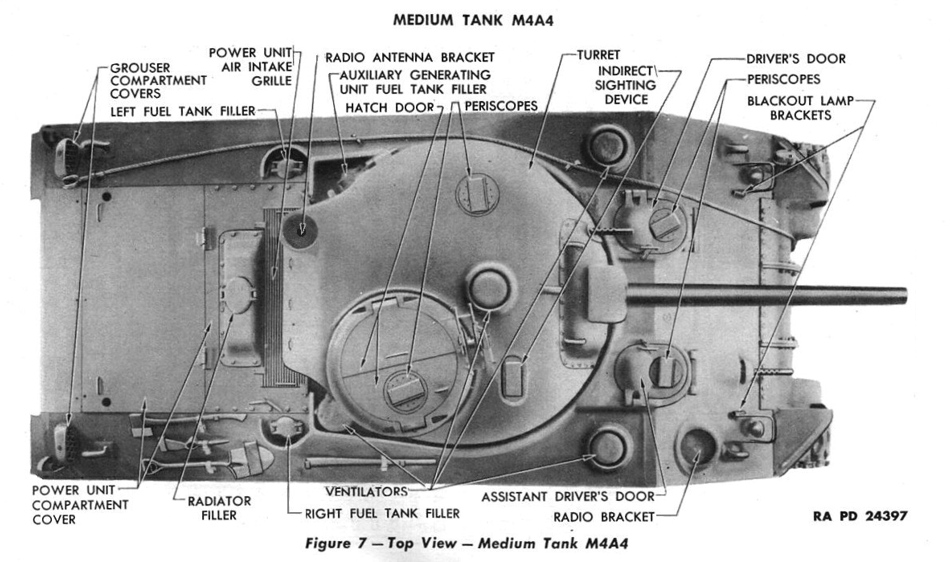
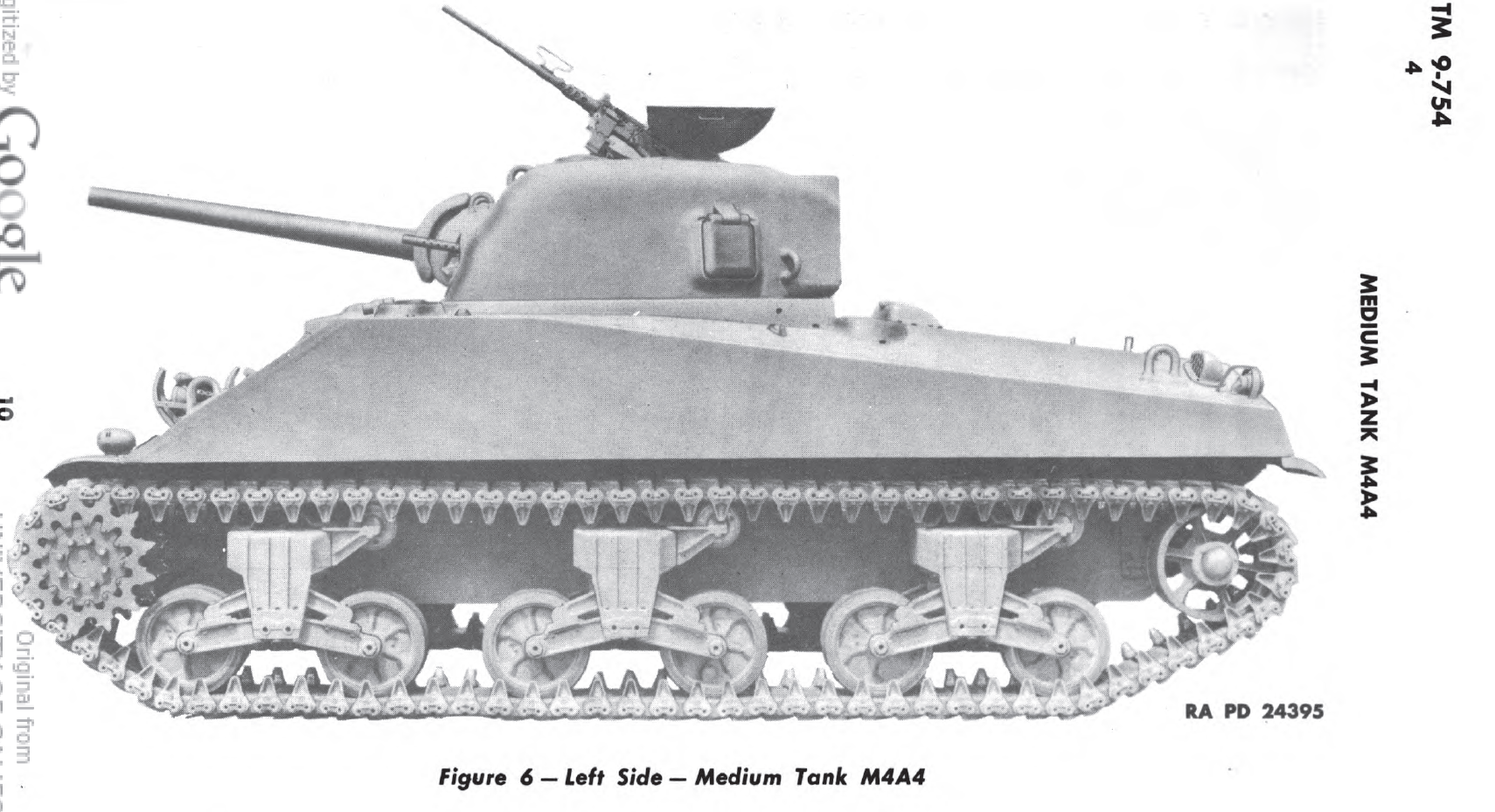
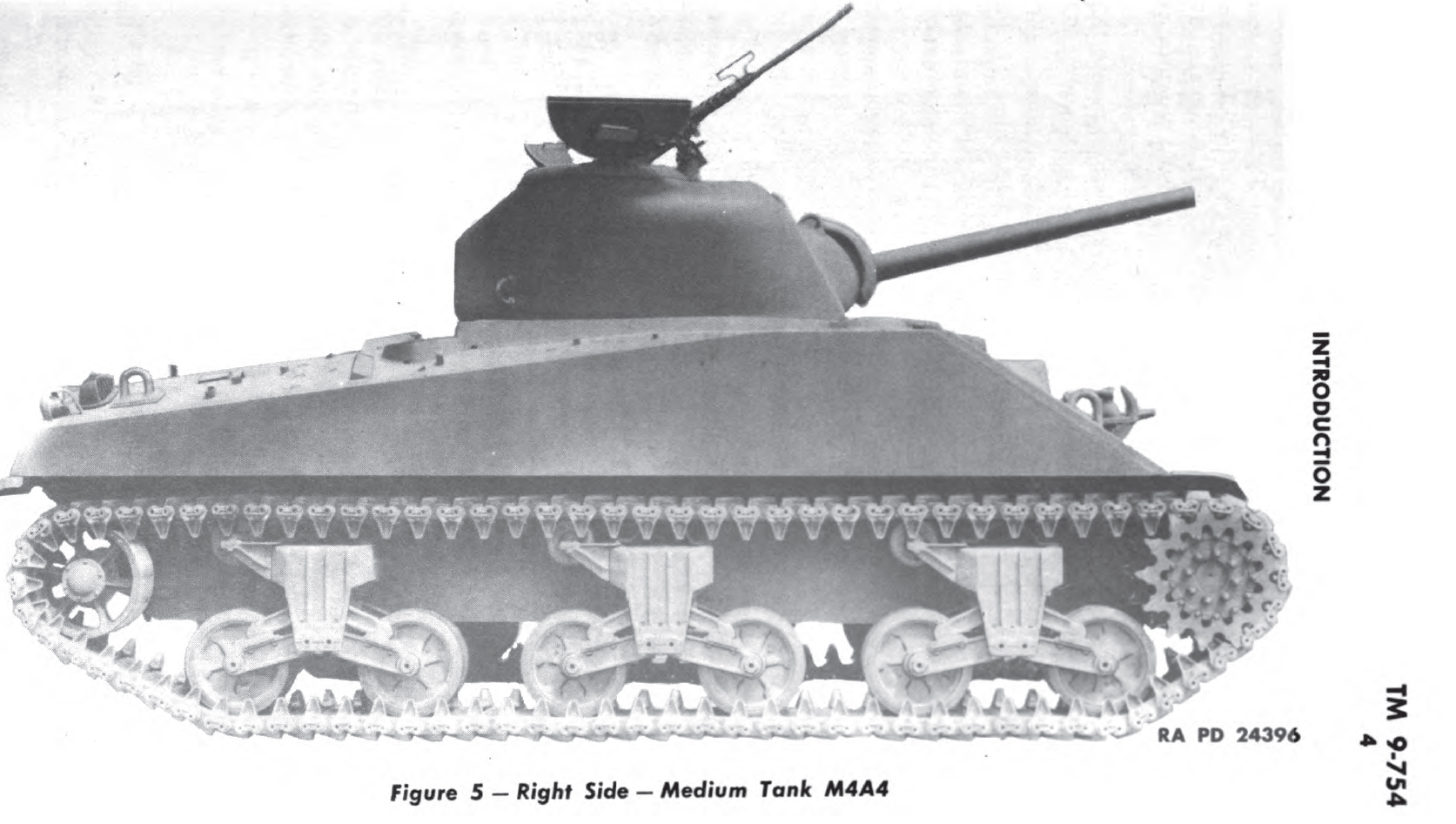
Links: Cool Sherman, Armor Related, Or WWII Web Sites
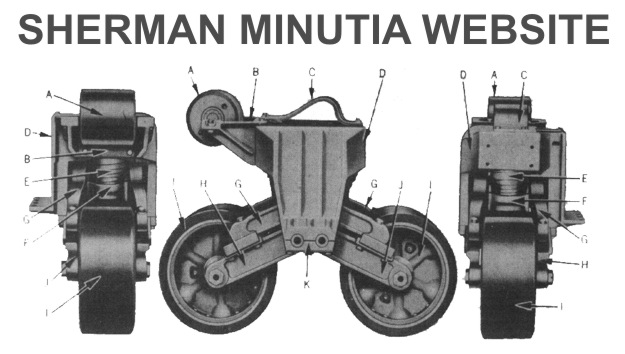
Sherman minutia site: You can spend days on this site learning interesting things about the Sherman. If you read through much of this site you will know how much I like the Sherman Minutia site because I mention it so much. It’s always open, and I can almost always find something new to read or something I forgot about on this site. Probably the best Sherman specific web site on the internet. If you want to know how to detect the differences between models, right down to specific factories unique fittings, this is the website to do it on, click the link and go, they are the best around for that! They are so good at it, I have no interest in ever trying to cover those details here!
Pierre-Olivier’s Photo Album from his Trip to America: You might be wondering why this is right below the Sherman minutia site link, oh well, maybe not, but if you were wondering, Pierre Olivier is the man responsible for the Sherman Minutia site. This is his photo album for his trip to the good old US of A. He checked out just about every armor museum in the US, and a lot of tanks in parks. I’d love to talk to him, I know he posts at Com-central.net, but for some reason I can’t get the registration to work there! I’ll figure it out, like tanknet, some legends of the Sherman world post there.
Tanks on Tarawa: I just picked up Tanks in Hell, A Marine Corps Tanks Company on Tarawa, by Oscar Gilbert and Romain Cansiere, and they mentioned this site in the acknowledgments section. I’ve only looked it over a little as of right now, (that will change, I’m sure the rest of my evening will be spent their), and right off the bat, I know the tank show in the water in my post on Tarawa has the wrong name in my post.
The Sherman Register, By Hanno Spoelstra: This site is an oldy but goody, and I can’t believe I forgot about it until Mr Spoelstra contacted me! Now I’ll be signing up to the mailing list!
The Sherman Tank Restoration page: A page that documents the restoration of a M4A3 76W HVSS tank that was surplused in the late 50s and purchased by Abdo S. Alan Co. a demolition company out of Oakland California. They used it to knock down buildings in Oakland for years. At some point the tank broke down, after being gutted for a new motor, and sat until the Littlefield collection purchased it, then traded it to someone who the current owner purchased it from. None of the previous owners had made any attempts to restore it. The current and last owner did an amazing job restoring the tank. Some surprises during the resto were, the tranny and final drives were in such good shape they required only cosmetic restoration. The suspension and tracks were also in very good shape. I spent more than three evenings going through this pages photo album of the restoration. This tank is a functioning work of art now.
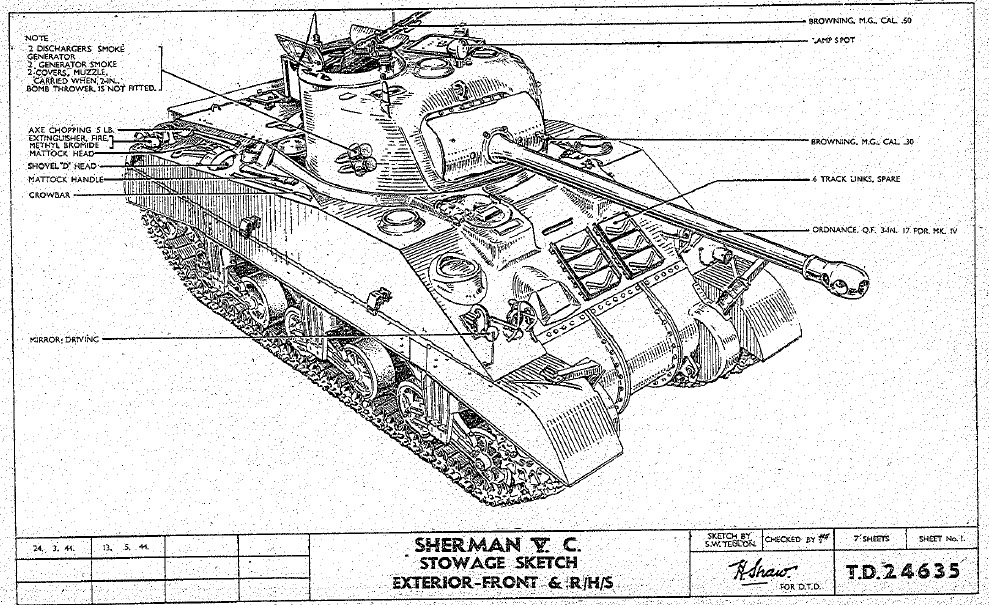
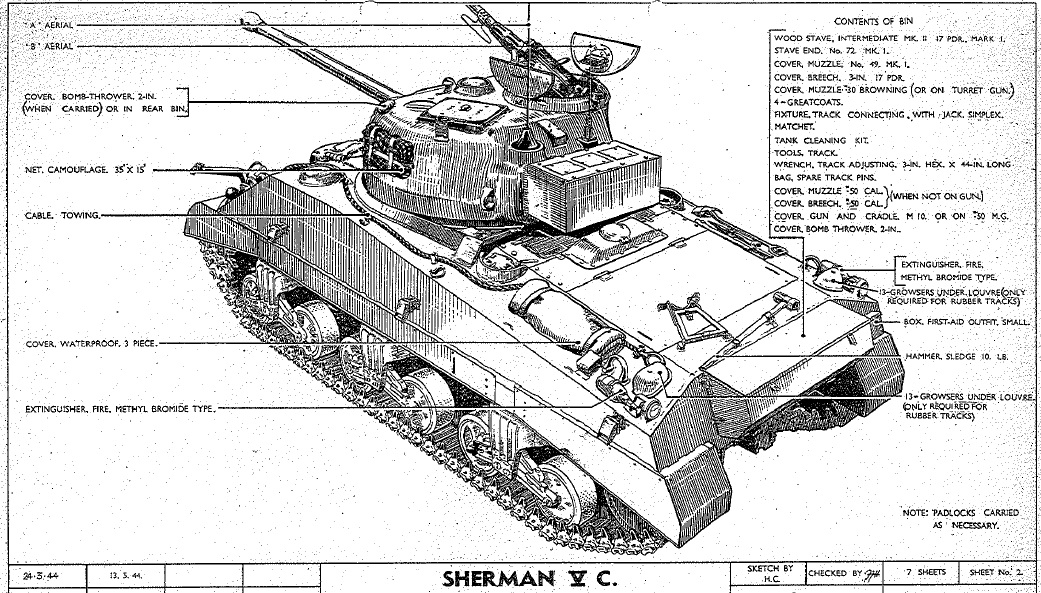
The Sherman Firefly Vc restoration page: This web page just went up and is about the restoration of the M4A4, which is the oldest known surviving A4 model. The tank served most of the war as a training tank in the US, until it was refurbished by Chrysler and shipped to the UK to be converted into a Sherman Vc firefly. They are just starting the restoration, and are collecting parts and researching the tank. I wish I could be of some kind of help, but I don’t know what I could do. But maybe if you stumble on this site, and happen to have Sherman stuff for sale, please contact them at this web page. The already have some fascinating information on how the tank was changed when converted to a Firefly, and how the interior was laid out. There is also some very interesting information on how the loaders job would have to be done. I plane to watch this page closely as they restore the old tank.
RamTank.CA: This website is to the RAM Tank, what the Sherman Tank Website is to the Sherman! Once you’ve read my article on the tank, and looked at the pretty pictures, check out their site to dig into the details!
Modeling the Sherman Tank in 1/72nd Scale: I just discovered this site, and it is a very nice site if you want to know about building Sherman tanks in the 1/72 scale. I have dabbled in this scale, but never came close to producing anything as nice at the author over there. The scale itself has come a long way and it’s really amazing what level of detail you can get in this scale, if you’re good with tweezers and your hands are steady!
General WWII or Tank Related Links:
The U.S. / American Automobile Industry in World War Two: This website. as its title suggests covers a lot of stuff along with the Shermans that were built by auto makers. There is more to building a tank than a single factory in many cases, and even a factory like CDA, that could do everything in house, farmed much of the subassemblies out to its normal sub contracts. This site gives info on many of them, and there is so much here, you could spend hours reading. I know I have! NEW LINK!
Tank and AFV news: A news website that covers Shermans when they hit the news. A generally interesting site if you are into tanks, and who isn’t! This is one of my read everyday sites.
The Lone Sentry: This website’s tag line is Photographs, documents, research on World War II, and that’s just what they do. This site is a staple of WWII history, and provides tons of good content. I was sad, this website went down for almost a month, but its back and stronger than ever.
Armor for the Ages: This is the website for the General George Patton Museum of Leadership, and the new National Armor and Cavalry Museum at Fort Benning. There are some very interest article and photo albums here, including one that documents the cosmetic restoration of the first Jumbo in Bastogne, Cobra King.
The AFV Database: This website has a huge listing of American Tank specifications, and he has a lot of very cool pictures to go with them. If you need some vehicle stats or images, this is your site! Some of the photos on this site were acquired there and the site owner was very nice about me using the images. Check his great site out. When I want data on an American tank, or AFV, his is my first stop.
Archive Awareness: A history site dedicated to translating Russian archive documents to english. He has done some very interesting posts on lend lease tanks, including the Lee and Sherman. This is a really great site, stuffed with great information.
Here is a specific link to a post on the Tiger versus the Shermans 75mm gun.
Toadman’s Tank pictures: Toadman’s tank pictures is one of those staples of the internet, I can’t believe I forgot to add him in the links. If you need close up shots of a tank, this is the place to go, if you want high res versions, he has CDs you can buy! Check out his site, there are a ton of Sherman photos up there.
The 8th Armored Division: The Thundering Herd, Association Website. While I was searching around on the internet for information on US Armored Divisions, this page came up, and was by far the most informative page on the subject. This Association has really done the 8th AD a service with this website, very informative.
The Internet Archive: This site is awesome, I’ve found so much interesting stuff there, everything from Technical Manuals to Unit Histories. I’ve literally downloaded hundreds of Sherman related documents from this site. Some of the hardest ones to find, I found here. If your going to donate to an internet site like Wikipedia, don’t and donate to this guys instead!
RadioNerds: This website was a huge help when I needed to find info about Sherman tank radios. They cover all US Army Radios, and also have an archive of PS Magazines, its a very cool site.
Panzerserra Bunker: A nice blog on modeling with some interesting Sherman stuff and very interesting plastic modeling techniques.
The Surviving Panzers site: This interesting site has PDFs for many of the major nations of WWIIs surviving tanks. For our purposes he has most of the Sherman models broken down into sub types and has a picture and short description of each tank. They are not complete, but they are close.
The Historical AFV Registry Home Page: This has registers of armored vehicles in several nations. The are in downloadable PDF and include a location for each vehicle.
M1919tech.com This new site is a very interesting look at the history of the M1919 machine gun. This is the machine gun used on the Sherman, and by the US Army and Marines during WWII. I learned a hell of a lot about the history of this machine gun than I knew before I found this site, it’s a great read with lots of rare photos.
AFV Photos: L&P Hannah’s great photo collection of Armor in the US. There are a lot of photos of tanks all over the US here. Paul Hannah must love tanks, he has traveled all over the United States taking pictures of them. I had no idea how many Sherman tanks there were in the east and mid west in parks and in front of VFW halls. This is another place you could spend hours browsing!
I remember interview: Of Dmitriy Loza, a Russian Tanker who used most lend Lease armor but the Sherman the most, he used both 75mm and 76mm version of the M4A2. This is a very interesting read, and shows how well the Russians liked the Shermans.
The Ford GAA engine Web Page: This Web site has some really fascinating information about the Ford GAA engine. Not much about its use in a tank, more about how it was just an amazing engine and could be used to make a lot of horsepower. The GAA motor was capable of a lot more than 500 horsepower, and was amazingly overbuilt, this page talks about why. If you’re a Hot-rodder, you will want to check it out.
Chieftain’s Hatch: His Sherman related hatches.
Wargaming’s The Chieftain, has what some might call a dream job, but when you hear how hard Wargaming works the poor guy, if you’re sane, you might feel different. For more details on the man, check out the WOT forums. For our purposes, and arguably the most important part of his job is Archive Crawling and then producing interesting article for far Wargaming to use to promote the game. As a fan of the game and history, I think this is great. The Chieftain has produced some very interesting articles on the Sherman tank or they are mentioned in others, so I will link to the ones important to the Sherman here.
Testing the British Cruisers: This Hatch is about testing the Centaur and Cromwell against a M4A3 Sherman. The Brits sent the two tanks over without much prep, and they were pretty new designs. As one could guess, the test went poorly for the British tanks. This caused some distress for the Brits, as did the Chieftains post on the forums. The post below answers some of the concerns of the angry posters.
Exercise Dracula: This was an extensive 2000 plus mile long test the British did testing the automotive reliability of the Cromwell, Centaur, and an M4A4 and M4A2 Sherman. Though not directly about the Sherman, it is very flattering to the Sherman, and in particular the M4A4 with is A57 multibank motor is considered very reliable!
Sherman PR, 1942: This Hatch contains a lot of glowing praise from the Brits about the Sherman and Lee tanks. This report is cherry picked for PR purposes of the time, but I bet they didn’t have to look around much for Brit tankers to praise the Sherman.
US Gyrostabiliser Issues: This Hatch is about the US Gyrostabiliser use or lack of it.
The US Army Tests Firefly: The hatch is about the US Army testing the British Firefly gun post war. Well not really since it was a Firefly turret installed on an M4A3 VVSS hull.
The Desert Sherman: This very interesting Hatch deals with the infrared night driving system and the odograph.
US Guns, German Armor, PT 1: This Hatch covers test of US guns on German Armor
US Guns, German Armor, PT2: Part two of the hatch above.
French Panthers: Or why a tank that can only go 150 kilometers sucks.
Nato Survey 1943: No, not that Nato, North African Theatre of operations. The Sherman gets mentioned but is not the focus.
Nato Survey 1943 Pt2: The rest of the above links story.
US Army Tanks in the Jungle Part, 1: This pair of Hatch’s are by guest writer, Harry Yeide, the author we know from the books section.
US Army Tanks in the Jungle Part, 2: This is part II by Harry Yeide.
The End of the M4(75): This Hatch is about the role the Sherman filled and how it was always designed to take out tanks. It’s also about the Army’s plan had always been to replace the 75mm gun with the 76mm gun, and this predates the D-Day landings.
US Army Tanks in Cities PT 1: This is another guest hatch by Harry Yeide, this series covering Shermans or or US Army tanks in Cities and Towns.
US Army Tanks in Cities PT 2: This is part two by the intrepid Harry Yeide!
The M4A2E4, the torsion bar Sherman: This hatch covers the M4A2E4 we covered in the Shermans of the Future section.
The Chieftains Hatch on the battle of El Alamein: The Chiefs take on this famous battle.
The Chieftains Hatch on the Battle of Peleliu: The Chiefs take on this famous battle.
The Chieftains Hatch on the battles for the Marianas: Saipan, the Japanese used tanks here, and the Chief covers it.
The Chieftains very interesting and detailed hatch on the battle of Tarawa: This is a tad less focused then how it was covered here, and overall probably a better account.